- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Glycerophosphate pathway control state
Description
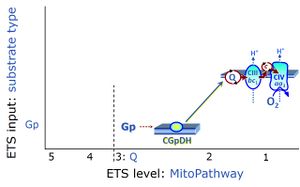
The glycerophosphate pathway control state (Gp) is an ET-pathway level 3 control state, supported by the fuel substrate glycerophosphate and electron transfer through glycerophosphate dehydrogenase Complex into the Q-junction. The glycerolphosphate shuttle represents an important pathway, particularly in liver and blood cells, of making cytoplasmic NADH available for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Cytoplasmic NADH reacts with dihydroxyacetone phosphate catalyzed by cytoplasmic glycerophos-phate dehydrogenase. On the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane, mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase oxidises glycerophosphate back to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, a reaction not generating NADH but reducing a flavin prosthesic group. The reduced flavoprotein donates its reducing equivalents to the electron transfer-pathway at the level of CoQ.
Abbreviation: Gp
Reference: Electron-transfer-pathway state, Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2016-01-25, edited 2016-11-19.
Gp(L)
Gp(P)
Gp(E)
Details
- Glycerophosphate oxidation is 10-fold higher in rabbit gracilis mitochondria (fast-twitch white muscle; 99% type IIb) compared to soleus (slow-twitch red muscle; 98% type I). Activity is comparatively low in human vastus lateralis. Glycerophosphate is an important substrate for respiration in brown adipose tissue mitochondria.
- Publications: Gp-pathway control state - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
Sort in ascending/descending order by a click on one of the small symbols in squares below. Default sorting: chronological. Empty fields appear first in ascending order.
| Year | Reference | Coupling | Pathway | Preparation | Organism | Tissue;cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korandova 2025 Anal Biochem | 2025 | Korandová Z, Pecina P, Pecinová A, Koňaříková E, Tesařová M, Houštěk J, Hansíková H, Ptáčková H, Zeman J, Honzík T, Mráček T (2025) Cryopreserved PBMCs can be used for the analysis of mitochondrial respiration and serve as a diagnostic tool for mitochondrial diseases. Anal Biochem 698:115745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2024.115745 | ET LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS | N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Cardoso 2025 Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis | 2025 | Cardoso LHD, Cecatto C, Ozola M, Korzh S, Zvejniece L, Gukalova B, Doerrier C, Dambrova M, Makrecka-Kuka M, Gnaiger E, Liepinsh E (2025) Fatty acid β-oxidation in brain mitochondria: Insights from high-resolution respirometry in mouse, rat and Drosophila brain, ischemia and aging models. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1871:167544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167544 | ET OXPHOS | F N S Gp | Homogenate | Mouse Rat Drosophila | Heart Nervous system Kidney |
| MiPNet21.14 Reference sample HRR | 2024-12-06 | Development of a reference sample for high-resolution respirometry. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | HEK |
| Hunter-Manseau 2024 Insect Sci | 2024 | Hunter-Manseau F, Cormier SB, Strang R, Pichaud N (2024) Fasting as a precursor to high-fat diet enhances mitochondrial resilience in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Sci [Epub ahead of print]. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.13355 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Al-Sabri 2024 Sci Rep | 2024 | Al-Sabri MH, Ammar N, Korzh S, Alsehli AM, Hosseini K, Fredriksson R, Mwinyi J, Williams MJ, Boukhatmi H, Schiöth HB (2024) Fluvastatin-induced myofibrillar damage is associated with elevated ROS, and impaired fatty acid oxidation, and is preceded by mitochondrial morphological changes. Sci Rep 14:3338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53446-w | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Mahapatra 2024 J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci | 2024 | Mahapatra G, Gao Z, Bateman JR 3rd, Lockhart SN, Bergstrom J, Piloso JE, Craft S, Molina AJA (2024) Peripheral blood cells from older adults exhibit sex-associated differences in mitochondrial function. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci [Epub ahead of print]. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glae098 | ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Jiang 2024 Nat Metab | 2024 | Jiang S, Yuan T, Rosenberger FA, Mourier A, Dragano NRV, Kremer LS, Rubalcava-Gracia D, Hansen FM, Borg M, Mennuni M, Filograna R, Alsina D, Misic J, Koolmeister C, Papadea P, de Angelis MH, Ren L, Andersson O, Unger A, Bergbrede T, Di Lucrezia R, Wibom R, Zierath JR, Krook A, Giavalisco P, Mann M, Larsson NG (2024) Inhibition of mammalian mtDNA transcription acts paradoxically to reverse diet-induced hepatosteatosis and obesity. Nat Metab [Epub ahead of print]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-01038-3 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp Other combinations | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Liver |
| Leo 2024 MitoFit | 2024 | Leo E, Rychtarova L, Garcia-Souza LF, Åsander Frostner E, Elmér E, Gnaiger E (2024) High-resolution respirometry in a small-volume chamber. MitoFit Preprints 2024.4.v2. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2024-0004.v2 - Accepted on 2024-10-27 as Manuscript JoVE67442R2 for publication in JoVE | ET LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Homogenate Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse | Heart Nervous system Blood cells HUVEC Platelet |
| Brunner 2024 Life Sci Alliance | 2024 | Brunner S, Höring M, Liebisch G, Schweizer S, Scheiber J, Giansanti P, Hidrobo M, Hermeling S, Oeckl J, Prudente de Mello N, Perocchi F, Seeliger C, Strohmeyer A, Klingenspor M, Plagge J, Küster B, Burkhardt R, Janssen KP, Ecker J (2024) Mitochondrial lipidomes are tissue specific - low cholesterol contents relate to UCP1 activity. Life Sci Alliance 7:e202402828. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202402828 | ET LEAK | N Gp ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Fat |
| Cardoso 2024 MitoFit FAO | 2024 | Cardoso LHD, Cecatto C, Ozola M, Korzh S, Zvejniece L, Gukalova B, Doerrier C, Dambrova M, Makrecka-Kuka M, Gnaiger E, Liepinsh E (2024) Fatty acid β-oxidation in brain mitochondria: Insights from high-resolution respirometry in mouse, rat and Drosophila brain, ischemia and aging models. MitoFit Preprints 2023.10. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2023-0010.v2 — Published 2024-10-17 BBA Mol Basis Dis (2025) | OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp | Homogenate | Mouse Rat Drosophila | Heart Nervous system Kidney |
| Allerton 2024 Sci Rep | 2024 | Allerton TD, Stampley JE, Li Z, Yu X, Quiariate H, Doiron JE, White G, Wigger Z, Gartia MR, Lefer DJ, Soto P, Irving BA (2024) Nitric oxide donors rescue metabolic and mitochondrial dysfunction in obese Alzheimer's model. Sci Rep 14:26118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-75870-8 | ET OXPHOS LEAK | N S NS Gp ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Batterson 2023 Physiol Rep | 2023 | Batterson PM, McGowan EM, Borowik AK, Kinter MT, Miller BF, Newsom SA, Robinson MM (2023) High-fat diet increases electron transfer flavoprotein synthesis and lipid respiration in skeletal muscle during exercise training in female mice. Physiol Rep 11:e15840. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.15840 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Skeletal muscle |
| Menail 2023 FASEB J | 2023 | Menail HA, Cormier SB, Léger A, Robichaud S, Hebert-Chatelain E, Lamarre SG, Pichaud N (2023) Age-related flexibility of energetic metabolism in the honey bee Apis mellifera. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202300654r | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | |
| Rodriguez 2023 BEC | 2023 | Rodríguez E, Bettinazzi S, Inwongwan S, Camus MF, Lane N (2023) Harmonizing protocols to measure Drosophila respiratory function in mitochondrial preparations. Bioenerg Commun 2023.3. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2023-0003 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp ROX | Permeabilized tissue Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Adant 2022 Mol Metab | 2022 | Adant I, Bird M, Decru B, Windmolders P, Wallays M, de Witte P, Rymen D, Witters P, Vermeersch P, Cassiman D, Ghesquière B (2022) Pyruvate and uridine rescue the metabolic profile of OXPHOS dysfunction. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101537 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Fibroblast |
| Nath 2022 Cell Rep | 2022 | Nath AS, Parsons BD, Makdissi S, Chilvers RL, Mu Y, Weaver CM, Euodia I, Fitze KA, Long J, Scur M, Mackenzie DP, Makrigiannis AP, Pichaud N, Boudreau LH, Simmonds AJ, Webber CA, Derfalvi B, Hammon Y, Rachubinski RA, Di Cara F (2022) Modulation of the cell membrane lipid milieu by peroxisomal β-oxidation induces Rho1 signaling to trigger inflammatory responses . Cell Rep 38:110433. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | ||
| Alencar 2022 MitoFit | 2022 | Alencar MB, Ramos EV, Silber AM, Zíková A, Oliveira MF (2022) The extraordinary energy metabolism of the bloodstream Trypanosoma brucei forms: a critical review and a hypothesis. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2022-0009.v2 — 2022-12-05 published in Bioenerg Commun 2022.17. | Gp | Protists | |||
| Pallag 2022 Int J Mol Sci | 2022 | Pallag G, Nazarian S, Ravasz D, Bui D, Komlódi T, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E, Seyfried TN, Chinopoulos C (2022) Proline oxidation supports mitochondrial ATP production when Complex I is inhibited. Int J Mol Sci 23:5111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095111 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Liver Kidney |
| Heimler 2022 BEC | 2022 | Heimler SR, Phang HJ, Bergstrom J, Mahapatra G, Dozier S, Gnaiger E, Molina AJA (2022) Platelet bioenergetics are associated with resting metabolic rate and exercise capacity in older adult women. Bioenerg Commun 2022.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0002 | OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Arbon 2022 Antimicrob Agents Chemother | 2022 | Arbon D, Ženíšková K, Šubrtová K, Mach J, Štursa J, Machado M, Zahedifard F, Leštinová T, Hierro-Yap C, Neuzil J, Volf P, Ganter M, Zoltner M, Zíková A, Werner L, Sutak R (2022) Repurposing of MitoTam: Novel anti-cancer drug candidate exhibits potent activity against major protozoan and fungal pathogens. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00727-22 | Gp | Intact cells | Protists | ||
| O'Hanlon 2022 Neurobiol Dis | 2022 | O'Hanlon ME, Tweedy C, Scialo F, Bass R, Sanz A, Smulders-Srinivasan TK (2022) Mitochondrial electron transport chain defects modify Parkinson's disease phenotypes in a Drosophila model. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105803 | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp CIV ROX | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Fuertes-Agudo 2022 Antioxidants (Basel) | 2022 | Fuertes-Agudo M, Luque-Tévar M, Cucarella C, Brea R, Boscá L, Quintana-Cabrera R, Martín-Sanz P, Casado M (2022) COX-2 expression in hepatocytes improves mitochondrial function after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. | OXPHOS ET | F N Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Liver |
| Chojnacka 2022 Mol Biol Cell | 2022 | Chojnacka KJ, Elancheliyan P, Mussulini BHM, Mohanraj K, Callegari S, Gosk A, Banach T, Góral T, Szczepanowska K, Rehling P, Serwa RA, Chacinska A (2022) Ovarian carcinoma immunoreactive antigen-like protein 2 (OCIAD2) is a novel complex III-specific assembly factor in mitochondria. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e21-03-0143 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | HEK |
| Alencar 2022 BEC | 2022 | Alencar MB, Ramos EV, Silber AM, Zíková A, Oliveira MF (2022) The extraordinary energy metabolism of the bloodstream Trypanosoma brucei forms: a critical review and hypothesis. Bioenerg Commun 2022.17. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0017 | Gp | Protists | |||
| Fernandez-Vizarra 2022 Cell Metab | 2022 | Fernández-Vizarra E, López-Calcerrada S, Sierra-Magro A, Pérez-Pérez R, Formosa LE, Hock DH, Illescas M, Peñas A, Brischigliaro M, Ding S, Fearnley IM, Tzoulis C, Pitceathly RDS, Arenas J, Martín MA, Stroud DA, Zeviani M, Ryan MT, Ugalde C (2022) Two independent respiratory chains adapt OXPHOS performance to glycolytic switch. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.005 | LEAK ET | N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | HEK |
| Horvath 2022 Antioxidants (Basel) | 2022 | Horváth G, Sváb G, Komlódi T, Ravasz D, Kacsó G, Doczi J, Chinopoulos C, Ambrus A, Tretter L (2022) Reverse and forward electron flow-induced H2O2 formation is decreased in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) subunit (E2 or E3) heterozygote knock out animals. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081487 | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system | |
| Rai 2022 G3 (Bethesda) | 2022 | Rai M, Carter SM, Shefali SA, Mahmoudzadeh NH, Pepin R, Tennessen JM (2022) The Drosophila melanogaster enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 is required for oogenesis, embryonic development, and amino acid homeostasis. G3 (Bethesda) 12:jkac115. https://doi.org/10.1093/g3journal/jkac115 | Gp | Drosophila | |||
| Schmidt 2021 Cancer Metab | 2021 | Schmidt CA, McLaughlin KL, Boykov IN, Mojalagbe R, Ranganathan A, Buddo KA, Lin CT, Fisher-Wellman KH, Neufer PD (2021) Aglycemic growth enhances carbohydrate metabolism and induces sensitivity to menadione in cultured tumor-derived cells. Cancer Metab 9:3. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Human | Liver |
| Rodriguez 2021 Front Genet | 2021 | Rodríguez E, Grover Thomas F, Camus MF, Lane N (2021) Mitonuclear interactions produce diverging responses to mild stress in Drosophila Larvae. Front Genet 12:734255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.734255 | ET LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Other cell lines |
| Hierro-Yap 2021 J Biol Chem | 2021 | Hierro-Yap C, Šubrtová K, Gahura O, Panicucci B, Dewar C, Chinopoulos C, Schnaufer A, Zíková A (2021) Bioenergetic consequences of FoF1-ATP synthase/ATPase deficiency in two life cycle stages of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem 296:100357. | Gp CIV | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Protists | ||
| Wall 2021 Dis Model Mech | 2021 | Wall JM, Basu A, Zunica ERM, Dubuisson OS, Pergola K, Broussard JP, Kirwan JP, Axelrod CL, Johnson AE (2021) CRISPR/Cas9-engineered Drosophila knock-in models to study VCP diseases. Dis Model Mech 14:dmm048603. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Antico 2021 Sci Adv | 2021 | Antico O, Ordureau A, Stevens M, Singh F, Nirujogi RS, Gierlinski M, Barini E, Rickwood ML, Prescott A, Toth R, Ganley IG, Harper JW, Muqit MMK (2021) Global ubiquitylation analysis of mitochondria in primary neurons identifies endogenous Parkin targets following activation of PINK1. Sci Adv 7:eabj0722. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Intact cells | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Fischer 2021 Antioxidants | 2021 | Fischer C, Volani C, Komlódi T, Seifert M, Demetz E, Valente de Souza L, Auer K, Petzer V, von Raffay L, Moser P, Gnaiger E, Weiss G (2021) Dietary iron overload and Hfe-/- related hemochromatosis alter hepatic mitochondrial function. Antioxidants 10:1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111818 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | ROX N S Gp | Mouse | Liver | |
| Palacka 2021 Int J Mol Sci | 2021 | Palacka P, Gvozdjáková A, Rausová Z, Kucharská J, Slopovský J, Obertová J, Furka D, Furka S, Singh KK, Sumbalová Z (2021) Platelet mitochondrial bioenergetics reprogramming in patients with urothelial carcinoma. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010388 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Platelet |
| Peruzzotti-Jametti 2021 PLoS Biol | 2021 | Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Bernstock JD, Willis CM, Manferrari G, Rogall R, Fernandez-Vizarra E, Williamson JC, Braga A, van den Bosch A, Leonardi T, Krzak G, Kittel A, Beninca C, Vicario N, Tan S, Bastos C, Bicci I, Iraci N, Smith JA, Peacock B, Muller KH, Lehner PJ, Buzas EI, Faria N, Zeviani M, Frezza C, Brisson A, Matheson NJ, Viscomi C, Pluchino S (2021) Neural stem cells traffic functional mitochondria via extracellular vesicles. PLoS Biol 19:3001166. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells | Mouse | Nervous system Stem cells |
| MiPNet21.17 BloodCellsIsolation | 2020-10-22 | O2k-Protocols: Isolation of blood cells for HRR. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells Platelet |
| Zussman 2020 J Autoimmun | 2020 | Zussman R, Xu LY, Damani T, Groom KM, Chen Q, Seers B, Viall CA, Chamley LW, Hickey A (2020) Antiphospholipid antibodies can specifically target placental mitochondria and induce ROS production. J Autoimmun 111:102437. | LEAK ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Human | Genital |
| Hayes 2020 Nutrients | 2020 | Hayes P, Fergus C, Ghanim M, Cirzi C, Burtnyak L, McGrenaghan CJ, Tuorto F, Nolan DP, Kelly VP (2020) Queuine micronutrient deficiency promotes Warburg metabolism and reversal of the mitochondrial ATP synthase in HeLa cells. Nutrients 12:E871. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | HeLa |
| MitoEAGLE blood cells 1 | 2020 | Åsander Frostner Eleonor*, Aburel Oana M*, Avram Vlad F*, Calabria Elisa, Castelo Rueda Maria Paulina*, Chamkha Imen*, Čižmárová Beata, Danila Maria-Daniela*, Doerrier Carolina*, Eckert Gunter P*, Ehinger Johannes K, Elmer Eskil*, Garcia-Souza Luiz F*, Gnaiger Erich*, Hoppel Florian*, Karabatsiakis Alexander*, Keppner Gloria, Kidere Dita*, Krako Jakovljević Nina, Labieniec-Watala Magdalena*, Lelcu Theia*, Micankova Petra, Michalak Slawomir*, Molina Anthony JA*, Pavlovic Kasja, Pichler Irene*, Piel Sarah, Rousar Tomas, Rybacka-Mossakowska Joanna, Schartner Melanie, Siewiera Karolina*, Silaidos Carmina*, Sjövall Fredrik*, Sobotka Ondrej*, Sumbalova Zuzana*, Swiniuch Daria, Vernerova Andrea*, Volani Chiara*, Vujacic-Mirski Ksenija*, Watala Cezary* (2020) Interlaboratory guide to mitochondrial respiratory studies with peripheral blood mononuclear cells and platelets. - Updated: 2020-03-06 - *Confirmed | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells Platelet |
| Stepanova 2020 Methods Cell Biol | 2020 | Stepanova A, Galkin A (2020) Measurement of mitochondrial H2O2 production under varying O2 tensions. Methods Cell Biol 155:273-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.12.008 | LEAK OXPHOS | S N Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Peruzzotti-Jametti 2020 bioRxiv | 2020 | Peruzzotti-Jametti L, Bernstock JD, Manferrari G, Rogall R, Fernandez-Vizarra E, Williamson JC, Braga A, van den Bosch A, Leonardi T, Kittel A, Benincá C, Vicario N, Tan S, Bastos C, Bicci I, Iraci N, Smith JA, Lehner PJ, Buzas EI, Faria N, Zeviani M, Frezza C, Brisson A, Matheson NJ, Viscomi C, Pluchino S (2020) Neural stem cells traffic functional mitochondria via extracellular vesicles to correct mitochondrial dysfunction in target cells. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.29.923441 . | LEAK | N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells | Mouse | Stem cells |
| Szibor 2020 J Biol Chem | 2020 | Szibor Marten, Gizatullina Zemfira, Gainutdinov Timur, Endres Thomas, Debska-Vielhaber Grazyna, Kunz Matthias, Karavasili Niki, Hallmann Kerstin, Schreiber Frank, Bamberger Alexandra, Schwarzer Michael, Doenst Torsten, Heinze Hans-Jochen, Leßmann Volkmar, Vielhaber Stefan, Kunz Wolfram S, Gellerich Frank Norbert (2020) Cytosolic, but not matrix, calcium is essential for adjustment of mitochondrial pyruvate supply. J Biol Chem 295:4383-97. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Frambach 2020 Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis | 2020 | Frambach SJCM, van de Wal MAE, van den Broek PHH, Smeitink JAM, Russel FGM, de Haas R, Schirris TJJ (2020) Effects of clofibrate and KH176 on life span and motor function in mitochondrial complex I-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866:165727. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Mouse | Skeletal muscle |
| Pajuelo-Reguera 2020 Cells | 2020 | Pajuelo Reguera David, Čunátová Kristýna, Vrbacký Marek, Pecinová Alena, Houštěk Josef, Mráček Tomáš, Pecina Petr (2020) Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform exchange results in modulation of oxygen affinity. Cells 9:E443. | OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS Other combinations | Permeabilized cells Oxidase;biochemical oxidation | Human | HEK |
| Stankova 2020 Int J Mol Sci | 2020 | Staňková P, Kučera O, Peterová E, Lotková H, Maseko TE, Nožičková K, Červinková Z (2020) Adaptation of mitochondrial substrate flux in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 21:E1101. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp NS ROX | Homogenate | Mouse | Liver |
| De-Souza 2020 J Biol Chem | 2020 | De-Souza EA, Pimentel FSA, De-Queiroz ALFV, Camara H, Felix-Formiga ML, Machado CM, Pinto S, Galina A, Mori MA, Montero-Lomelí M, Masuda CA (2020) The yeast protein Ubx4p contributes to mitochondrial respiration and lithium-galactose-mediated activation of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem 295:3773-82. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp NS ROX | Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Caenorhabditis elegans Saccharomyces cerevisiae | |
| Friederich-Persson 2020 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol | 2020 | Friederich-Persson M, Persson P (2020) Mitochondrial angiotensin II receptors regulate oxygen consumption in kidney mitochondria from healthy and type 1 diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 318:F683-88. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Kidney |
| Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways | 2020 | Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse | Heart Skeletal muscle Fibroblast |
| BEC 2020.1 doi10.26124bec2020-0001.v1 | 2020 | Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp DQ CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | ||
| Rodriguez 2020 J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci | 2020 | Rodríguez E, Hakkou M, Hagen TM, Lemieux H, Blier PU (2020) Divergences in the control of mitochondrial respiration are associated with lifespan variation in marine bivalves. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 76:796-804. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Molluscs | |
| Contreras Mostazo 2020 Cancers (Basel) | 2020 | Mostazo MGC, Kurrle N, Casado M, Fuhrmann D, Alshamleh I, Häupl B, Martín-Sanz P, Brüne B, Serve H, Schwalbe H, Schnütgen F, Marin S, Cascante M (2020) Metabolic plasticity is an essential requirement of acquired tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancers (Basel) 12:E3443. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Blood cells |
| McLaughlin 2020b Sci Rep | 2020 | McLaughlin KL, Hagen JT, Coalson HS, Nelson MAM, Kew KA, Wooten AR, Fisher-Wellman KH (2020) Novel approach to quantify mitochondrial content and intrinsic bioenergetic efficiency across organs. Sci Rep 10:17599. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart Liver Kidney Fat |
| Simard 2020b Metabolites | 2020 | Simard CJ, Touaibia M, Allain EP, Hebert-Chatelain E, Pichaud N (2020) Role of the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier in the occurrence of metabolic inflexibility in Drosophila melanogaster exposed to dietary sucrose. Metabolites 10:E411. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Simard 2020 Metabolites | 2020 | Simard C, Lebel A, Allain EP, Touaibia M, Hebert-Chatelain E, Pichaud N (2020) Metabolic characterization and consequences of mitochondrial pyruvate carrier deficiency in Drosophila melanogaster. Metabolites 109:E363. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Pajuelo 2020 Cells | 2020 | Pajuelo Reguera D, Čunátová K, Vrbacký M, Pecinová A, Houštěk J, Mráček T, Pecina P (2020) Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform exchange results in modulation of oxygen affinity. Cells 9:443. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | HEK |
| Lin 2020 Preprints | 2020 | Lin M, Fu T, Hsu C, Huang S, Lin Y, Wang J (2020) Cycling exercise training enhances mitochondrial bioenergetics of platelets in patients with peripheral arterial disease: a randomized controlled trial. Preprints 2020070567. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Platelet |
| Dawid 2020 Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg | 2020 | Dawid C, Weber D, Musiol E, Janas V, Baur S, Lang R, Fromme T (2020) Comparative assessment of purified saponins as permeabilization agents during respirometry. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1861:148251. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse | Nervous system HEK |
| Politis-Barber 2020 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab | 2020 | Politis-Barber V, Brunetta HS, Paglialunga S, Petrick HL, Holloway GP (2020) Long-term high-fat feeding exacerbates short-term increases in adipose mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, without impairing mitochondrial respiration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 319:E376-87. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N Gp NS | Permeabilized cells | Mouse | Fat |
| Dolezelova 2020 PLoS Biol | 2020 | Doleželová E, Kunzová M, Dejung M, Levin M, Panicucci B, Regnault C, Janzen CJ, Barrett MP, Butter F, Zíková A (2020) Cell-based and multi-omics profiling reveals dynamic metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive developmental progression of Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS Biol 18:e3000741. | LEAK ROUTINE | S Gp CIV | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Protists | |
| Coppin 2020 Cell Death Dis | 2020 | Coppin L, Jannin A, Ait Yahya E, Thuillier C, Villenet C, Tardivel M, Bongiovanni A, Gaston C, de Beco S, Barois N, van Seuningen I, Durand E, Bonnefond A, Vienne JC, Vamecq J, Figeac M, Vincent A, Delacour D, Porchet N, Pigny P (2020) Galectin-3 modulates epithelial cell adaptation to stress at the ER-mitochondria interface. Cell Death Dis 11:360. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Islet cell;pancreas;thymus Endothelial;epithelial;mesothelial cell |
| Electron-transfer-pathway state | 2019 | Gnaiger E (2019) ET-pathway states. Mitochondr Physiol Network 2019-06-11 (last edit since 2016-11-08). | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria SMP | ||
| Tiebe 2019 Sci Rep | 2019 | Tiebe M, Lutz M, Senyilmaz Tiebe D, Teleman AA (2019) Crebl2 regulates cell metabolism in muscle and liver cells. Sci Rep 9:19869. | LEAK OXPHOS ROUTINE | F N Gp ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Mouse | Skeletal muscle Liver |
| Hsu 2019 J Clin Med | 2019 | Hsu CC, Tsai HH, Fu TC, Wang JS (2019) Exercise training enhances platelet mitochondrial bioenergetics in stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med 8:E2186. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Platelet Blood cells |
| Robinson 2019 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol | 2019 | Robinson MM, Sather BK, Burney ER, Ehrlicher SE, Stierwalt HD, Franco MC, Newsom SA (2019) Robust intrinsic differences in mitochondrial respiration and H2O2 emission between L6 and C2C12 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 317:C339-C347. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells | Mouse Rat | Skeletal muscle |
| Bahhir 2019 PLoS Genet | 2019 | Bahhir D, Yalgin C, Ots L, Jaervinen S, George J, Naudi A, Krama T, Krams I, Tamm M, Andjelkovic A, Dufour E, Gonzalez de Cozar JM, Gerards M, Parhiala M, Pamplona R, Jacobs HT, Joers P (2019) Manipulating mtDNA in vivo reprograms metabolism via novel response mechanisms. PLoS Genet 15:e1008410. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp CIV ROX | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Silva Ramos 2019 PLoS Genet | 2019 | Silva Ramos E, Motori E, Brüser C, Kühl I, Yeroslaviz A, Ruzzenente B, Kauppila JHK, Busch JD, Hultenby K, Habermann BH, Jakobs S, Larsson NG, Mourier A (2019) Mitochondrial fusion is required for regulation of mitochondrial DNA replication. PLoS Genet 15:e1008085. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp | Permeabilized cells Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart Fibroblast |
| Gonzalez-Armenta 2019 J Nutr | 2019 | Gonzalez-Armenta JL, Gao Z, Appt SE, Vitolins MZ, Michalson KT, Register TC, Shively CA, Molina AJA (2019) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration is elevated in female cynomolgus macaques fed a western compared with a mediterranean diet. J Nutr 149:1493-502. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Other mammals | Skeletal muscle |
| Bettinazzi 2019 Cryobiology | 2019 | Bettinazzi S, Gendron AD, Breton S (2019) The effect of cryopreservation on mitochondrial function in freshwater mussel tissue samples (Bivalvia: Unionida). Cryobiology 88:106-109. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV NS ROX S Other combinations | Permeabilized tissue | Molluscs | Lung;gill |
| De-Souza-Ferreira 2019 J Neurochem | 2019 | de-Souza-Ferreira E, Rios-Neto IM, Martins EL, Galina A (2019) Mitochondria-coupled glucose phosphorylation develops after birth to modulate H2O2 release and calcium handling in rat brain. J Neurochem 149:624-40. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV NS | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Nervous system |
| Gaviraghi 2019 Anal Biochem | 2019 | Gaviraghi A, Oliveira MF (2019) A method for assessing mitochondrial physiology using mechanically permeabilized flight muscle of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Anal Biochem 576:33-41. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Cormier 2019 Sci Rep | 2019 | Cormier RPJ, Champigny CM, Simard CJ, St-Coeur PD, Pichaud N (2019) Dynamic mitochondrial responses to a high-fat diet in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci Rep 9:4531. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS ROX CIV | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Douros 2019 JCI Insight | 2019 | Douros JD, Niu J, Sdao SM, Gregg T, Fisher-Wellman KH, Bharadwaj MS, Molina A, Arumugam R, Martin MD, Petretto E, Merrins MJ, Herman MA, Tong J, Campbell JE, D'Alessio D (2019) Sleeve gastrectomy rapidly enhances islet function independently of body weight. JCI Insight 4:126688. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue | Mouse | Islet cell;pancreas;thymus |
| Pichaud 2019 Front Genet | 2019 | Pichaud N, Bérubé R, Côté G, Belzile C, Dufresne F, Morrow G, Tanguay RM, Rand DM, Blier PU (2019) Age dependent dysfunction of mitochondrial and ROS metabolism induced by mitonuclear mismatch. Front Genet 10:130. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Hedges 2019 Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol | 2019 | Hedges CP, Wilkinson RT, Devaux JBL, Hickey AJR (2019) Hymenoptera flight muscle mitochondrial function: Increasing metabolic power increases oxidative stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 230:115-21. | OXPHOS ET LEAK | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Other invertebrates | Skeletal muscle |
| Fisher-Wellman 2019 Cell Rep | 2019 | Fisher-Wellman KH, Draper JA, Davidson MT, Williams AS, Narowski TM, Slentz DH, Ilkayeva OR, Stevens RD, Wagner GR, Najjar R, Hirschey MD, Thompson JW, Olson DP, Kelly DP, Koves TR, Grimsrud PA, Muoio DM (2019) Respiratory phenomics across multiple models of protein hyperacylation in cardiac mitochondria reveals a marginal impact on bioenergetics. Cell Rep 26:1557-72. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart Skeletal muscle |
| Bettinazzi 2019 Proc Biol Sci | 2019 | Bettinazzi S, Rodríguez E, Milani L, Blier PU, Breton S (2019) Metabolic remodelling associated with mtDNA: insights into the adaptive value of doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria. Proc Biol Sci 286:20182708. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Molluscs | Lung;gill Genital |
| MiPNet21.06 SUIT RP | 2018-06-25 | SUIT reference protocol for OXPHOS analysis by high-resolution respirometry. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | ||
| Clarke 2018 Methods Mol Biol | 2018 | Clarke KJ, Porter RK (2018) The importance of calcium ions for determining mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity when measuring uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) function in mitochondria isolated from brown adipose tissue. Methods Mol Biol 1782:325-36. | LEAK | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Fat |
| Jang 2018 Intensive Care Med Exp | 2018 | Jang DH, Khatri UG, Shortal BP, Kelly M, Lambert DS, Hardy K, Eckmann DM (2018) Alterations in mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species in patients poisoned with carbon monoxide treated with hyperbaric oxygen. Intensive Care Med Exp 6:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-018-0169-2 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Allard 2018 J Clin Endocrinol Metab | 2018 | Allard NAE, Schirris TJJ, Verheggen RJ, Russel FGM, Rodenburg RJ, Smeitink JAM, Thompson PD, Hopman MTE, Timmers S (2018) Statins affect skeletal muscle performance: evidence for disturbances in energy metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:75-84. | OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV NS | Permeabilized tissue | Human | Skeletal muscle |
| Simard 2018 J Vis Exp | 2018 | Simard CJ, Pelletier G, Boudreau LH, Hebert-Chatelain E, Pichaud N (2018) Measurement of mitochondrial oxygen consumption in permeabilized fibers of Drosophila using minimal amounts of tissue. J Vis Exp 134. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Jang 2018 J Med Toxicol | 2018 | Jang DH, Khatri UG, Mudan A, Love JS, Owiredu S, Eckmann DM (2018) Translational application of measuring mitochondrial functions in blood cells obtained from patients with acute poisoning. J Med Toxicol 14:144-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13181-018-0656-6 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Oemer 2018 Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A | 2018 | Oemer G, Lackner L, Muigg K, Krumschnabel G, Watschinger K, Sailer S, Lindner H, Gnaiger E, Wortmann SB, Werner ER, Zschocke J, Keller MA (2018) The molecular structural diversity of mitochondrial cardiolipins. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 115:4158-63. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719407115 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | HeLa |
| Doerrier 2018 Methods Mol Biol | 2018 | Doerrier C, Garcia-Souza LF, Krumschnabel G, Wohlfarter Y, Mészáros AT, Gnaiger E (2018) High-Resolution FluoRespirometry and OXPHOS protocols for human cells, permeabilized fibers from small biopsies of muscle, and isolated mitochondria. Methods Mol Biol 1782:31-70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7831-1_3 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse Rat Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Heart Skeletal muscle Endothelial;epithelial;mesothelial cell Blood cells HEK Platelet |
| Perks 2018 Cell Rep | 2018 | Perks KL, Rossetti G, Kuznetsova I, Hughes LA, Ermer JA, Ferreira N, Busch JD, Rudler DL, Spahr H, Schöndorf T, Shearwood AJ, Viola HM, Siira SJ, Hool LC, Milenkovic D, Larsson NG, Rackham O, Filipovska A (2018) PTCD1 is required for 16S rRNA maturation complex stability and mitochondrial ribosome assembly. Cell Rep 23:127-42. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp S | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart |
| Monaco 2018b Diabetologia | 2018 | Monaco CMF, Hughes MC, Ramos SV, Varah NE, Lamberz C, Rahman FA, McGlory C, Tarnopolsky MA, Krause MP, Laham R, Hawke TJ, Perry CGR (2018) Altered mitochondrial bioenergetics and ultrastructure in the skeletal muscle of young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 61:1411-23. | OXPHOS | N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Human | Skeletal muscle |
| Boutoual 2018 Scientific Reports | 2018 | Boutoual, R., Meseguer, S., Villarroya, M., Martin-Hernandez, E., Errami, M., Martin, M. A., Casado, M., and Armengod, M. E. (2018) Defects in the mitochondrial-tRNA modification enzymes MTO1 and GTPBP3 promote different metabolic reprogramming through a HIF-PPARgamma-UCP2-AMPK axis. Scientific reports 8, 1163 | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F S Gp | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Other cell lines Fibroblast |
| Burney 2018 Thesis | 2018 | Burney E (2018) Characterization of mitochondrial metabolism in L6 rat myoblasts. Bachelor's Thesis p50. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Rat | Other cell lines |
| Komlodi 2018 J Bioenerg Biomembr | 2018 | Komlódi T, Geibl FF, Sassani M, Ambrus A, Tretter L (2018) Membrane potential and delta pH dependency of reverse electron transport-associated hydrogen peroxide production in brain and heart mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 50:355-365 | LEAK | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Guinea pig | Heart Nervous system |
| Thompson 2018 EMBO Mol Med | 2018 | Thompson K, Mai N, Oláhová M, Scialó F, Formosa LE, Stroud DA, Garrett M, Lax NZ, Robertson FM, Jou C, Nascimento A, Ortez C, Jimenez-Mallebrera C, Hardy SA, He L, Brown GK, Marttinen P, McFarland R, Sanz A, Battersby BJ, Bonnen PE, Ryan MT, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM, Lightowlers RN, Taylor RW (2018) OXA1L mutations cause mitochondrial encephalopathy and a combined oxidative phosphorylation defect. EMBO Mol Med 10:e9060. | LEAK OXPHOS | N CIV ROX Gp Other combinations | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Champigny 2018 Mar Drugs | 2018 | Champigny CM, Cormier RPJ, Simard CJ, St-Coeur PD, Fortin S, Pichaud N (2018) Omega-3 monoacylglyceride effects on longevity, mitochondrial metabolism and oxidative stress: insights from Drosophila melanogaster. Mar Drugs 16:E453. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S NS ROX Gp | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Lobo-Jarne 2018 Cell Rep | 2018 | Lobo-Jarne T, Nývltová E, Pérez-Pérez R, Timón-Gómez A, Molinié T, Choi A, Mourier A, Fontanesi F, Ugalde C, Barrientos A (2018) Human COX7A2L regulates complex III biogenesis and promotes supercomplex organization remodeling without affecting mitochondrial bioenergetics. Cell Rep 25:1786-99. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S NS ROX Gp | Permeabilized cells | Human | HEK Other cell lines |
| Stepanova 2018 J Neurochem | 2018 | Stepanova A, Konrad C, Manfredi G, Springett R, Ten V, Galkin A (2018) The dependence of brain mitochondria reactive oxygen species production on oxygen level is linear, except when inhibited by antimycin A. J Neurochem 148:731-45. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp NS ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Mahapatra 2018 Clin Sci (Lond) | 2018 | Mahapatra G, Smith SC, Hughes TM, Wagner B, Maldjian JA, Freedman BI, Molina AJA (2018) Blood-based bioenergetic profiling is related to differences in brain morphology in African Americans with Type 2 diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond) 132:2509-18. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20180690 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Nervous system Blood cells |
| Lal 2018 Springer | 2018 | Lal MA (2018) Respiration. In: Bhatla SC, Lal MA (eds) Plant physiology, development and metabolism. Springer, Singapore:253-314. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2023-1_7 | S Gp | ||||
| Efimova 2018 Thesis | 2018 | Efimova I (2018) Structural composition and functional properties of mitochondrial FoF1 ATP synthase on models of specific subunits deficiencies. PhD Thesis 94. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | HEK |
| Masson 2017 Sci Rep | 2017 | Masson SWC, Hedges CP, Devaux JBL, James CS, Hickey AJR (2017) Mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate facilitates bumblebee pre-flight thermogenesis. Sci Rep 7:13107. | OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Jeong 2017 Exp Mol Med | 2017 | Jeong JH, Cheol Kang Y, Piao Y, Kang S, Pak YK (2017) miR-24-mediated knockdown of H2AX damages mitochondria and the insulin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med 49:e313. | OXPHOS | N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Liver |
| Chretien 2017 bioRxiv | 2017 | Chretien D, Benit P, Ha HH, Keipert S, El-Khoury R, Chang YT, Jastroch M, Jacobs H, Rustin P, Rak M (2017) Mitochondria are physiologically maintained at close to 50 C. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/133223 . | OXPHOS | Gp | Permeabilized cells | HEK | |
| Kake-Guena 2017 J Therm Biol | 2017 | Kake-Guena SA, Touisse K, Warren BE, Scott KY, Blier PU, Lemieux H (2017) Temperature-related differences in mitochondrial function among clones of the cladoceran Daphnia pulex. J Therm Biol 69:23-31. | LEAK OXPHOS | S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Crustaceans | |
| Pecinova 2017 Oxid Med Cell Longev | 2017 | Pecinova A, Drahota Z, Kovalcikova J, Kovarova N, Pecina P, Alan L, Zima M, Houstek J, Mracek T (2017) Pleiotropic effects of biguanides on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Oxid Med Cell Longev 7038603. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Fat |
| Permer 2017 Bachelor Thesis | 2017 | Permer M (2017) Respirometrische Charakterisierung kryopräservierter HEK 239T Zellen. Bachelor Thesis 1-56. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Other cell lines HEK |
| Schreiber 2017 Cell Metab | 2017 | Schreiber R, Diwoky C, Schoiswohl G, Feiler U, Wongsiriroj N, Abdellatif M, Kolb D, Hoeks J, Kershaw EE, Sedej S, Schrauwen P, Haemmerle G, Zechner R (2017) Cold-induced thermogenesis depends on ATGL-mediated lipolysis in cardiac muscle, but not brown adipose tissue. Cell Metab 26:753-63. | LEAK | N Gp | Homogenate | Mouse | Fat |
| Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque 2017 Mol Neurobiol | 2017 | Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque JP, de Souza Ferreira E, de Carvalho DP, Galina A (2017) Mitochondria-bound hexokinase (mt-HK) activity differ in cortical and hypothalamic synaptosomes: differential role of mt-HK in H2O2 depuration. Mol Neurobiol 55:5889-5900. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp ROX | Intact cells | Rat | Nervous system |
| Comelli 2017 J Bioenerg Biomembr | 2017 | Comelli M, Pretis I, Buso A, Mavelli I (2017) Mitochondrial energy metabolism and signalling in human glioblastoma cell lines with different PTEN gene status. J Bioenerg Biomembr 50:33-52. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | Nervous system |
| Categories of SUIT protocols | 2017 | Gnaiger E (2017) Categories of SUIT protocols and ETS pathway control states. MiPNet 2017-03-12; original 2016-03-20; edited 2016-08-21. | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | ||||
| Rana 2017 Nat Commun | 2017 | Rana A, Oliveira MP, Khamoui AV, Aparicio R, Rera M, Rossiter HB, Walker DW (2017) Promoting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission in midlife prolongs healthy lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00525-4 | OXPHOS | N Gp NS | Drosophila | ||
| MiPNet21.07 MitoFit DatLab PT | 2016-07-20 | MitoFit DatLab proficiency test. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | |
| Wolff 2016 J Evol Biol | 2016 | Wolff JN, Pichaud N, Camus MF, Côté G, Blier PU, Dowling DK (2016) Evolutionary implications of mitochondrial genetic variation: mitochondrial genetic effects on OXPHOS respiration and mitochondrial quantity change with age and sex in fruit flies. J Evol Biol 29:736-47. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Newell 2016 Physiol Entomol | 2016 | Newell C, Kane CL, Kane DC (2016) Mitochondrial substrate specificity in beetle flight muscle: assessing respiratory oxygen flux in small samples from Dermestes maculatus and Tenebrio molitor. Physiol Entomol p7. | OXPHOS | F N Gp Other combinations | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Scialo 2016 Cell Metab | 2016 | Scialò F, Sriram A, Fernández-Ayala D, Gubina N, Lõhmus M, Nelson G, Logan A, Cooper HM, Navas P, Enríquez JA, Murphy MP, Sanz A (2016) Mitochondrial ROS produced via reverse electron transport extend animal lifespan. Cell Metab 23:725-34. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Teulier 2016 Proc Biol Sci | 2016 | Teulier L, Weber JM, Crevier J, Darveau CA (2016) Proline as a fuel for insect flight: enhancing carbohydrate oxidation in hymenopterans. Proc Biol Sci 283: 20160333. | OXPHOS | F N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Silva Ramos 2016 Biochim Biophys Acta | 2016 | Silva Ramos E, Larsson NG, Mourier A (2016) Bioenergetic roles of mitochondrial fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1857:1277-83. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | S Gp | Permeabilized cells | Mouse | Fibroblast |
| Lark 2016 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol | 2016 | Lark DS, Torres MJ, Lin CT, Ryan TE, Anderson EJ, Neufer PD (2016) Direct real-time quantification of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation efficiency in permeabilized skeletal muscle myofibers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 311:C239-45. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Skeletal muscle |
| Chakraborty 2016 Pancreatology | 2016 | Chakraborty M, Hickey AJ, Petrov MS, Macdonald JR, Thompson N, Newby L, Sim D, Windsor JA, Phillips AR (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in early experimental and clinical acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 16:739-47. | LEAK OXPHOS ROUTINE ET | N Gp CIV NS ROX S | Permeabilized cells | Human Rat | Blood cells |
| Hartmannova 2016 Hum Mol Genet | 2016 | Hartmannová H, Piherová L, Tauchmannová K, Kidd K, Acott PD, Crocker JF, Oussedik Y, Mallet M, Hodaňová K, Stránecký V, Přistoupilová A, Barešová V, Jedličková I, Živná M, Sovová J, Hůlková H, Robins V, Vrbacký M, Pecina P, Kaplanová V, Houštěk J, Mráček T, Thibeault Y, Bleyer AJ, Kmoch S (2016) Acadian variant of Fanconi syndrome is caused by mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I deficiency due to a non-coding mutation in complex I assembly factor NDUFAF6. Hum Mol Genet 25:4062-79. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Fibroblast |
| Scialo 2016 PLOS ONE | 2016 | Scialo F, Sriram A, Stefanatos R, Sanz A (2016) Practical recommendations for the use of the GeneSwitch Gal4 system to knock-Down genes in Drosophila melanogaster. PLOS ONE 11:e0161817. | LEAK OXPHOS | N CIV Other combinations ROX Gp | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Rovenko 2015 Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol | 2015 | Rovenko BM, Kubrak OI, Gospodaryov DV, Yurkevych IS, Sanz A, Lushchak OV, Lushchak VI (2015) Restriction of glucose and fructose causes mild oxidative stress independently of mitochondrial activity and reactive oxygen species in Drosophila melanogaster. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 187:27-39. | OXPHOS | N Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Ramos-Filho 2015 PLoS One | 2015 | Ramos-Filho D, Chicaybam G, de-Souza-Ferreira E, Guerra Martinez C, Kurtenbach E, Casimiro-Lopes G, Galina A (2015) High intensity interval training (HIIT) induces specific changes in respiration and electron leakage in the mitochondria of different rat skeletal muscles. PLoS One 10:e0131766. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Skeletal muscle |
| Syrjanen 2015 Front Zool | 2015 | Syrjanen L, Valanne S, Kuuslahti M, Tuomela T, Sriram A, Sanz A, Jacobs HT, Ramet M, Parkkila S. (2015) β carbonic anhydrase is required for female fertility in Drosophila melanogaster. Front Zool 12:19. | OXPHOS | N Gp CIV Other combinations | Homogenate | Drosophila | |
| Schirris 2015 Cell Metab | 2015 | Schirris TJ, Renkema GH, Ritschel T, Voermans NC, Bilos A, van Engelen BG, Brandt U, Koopman WJ, Beyrath JD, Rodenburg RJ, Willems PH, Smeitink JA, Russel FG (2015) Statin-induced myopathy is associated with mitochondrial complex III inhibition. Cell Metab 22:399-407. | ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human Mouse | Skeletal muscle Other cell lines |
| Patil 2015 J Nutr Biochem | 2015 | Patil YN, Dille KN, Burk DH, Cortez CC, Gettys TW (2015) Cellular and molecular remodeling of inguinal adipose tissue mitochondria by dietary methionine restriction. J Nutr Biochem 26:1235-47. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Skeletal muscle Liver Fat |
| Jiroutkova 2015 Crit Care | 2015 | Jiroutková K, Krajčová A, Ziak J, Fric M, Waldauf P, Džupa V, Gojda J, Němcova-Fürstová V, Kovář J, Elkalaf M, Trnka J, Duška F (2015) Mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle of patients with protracted critical illness and ICU-acquired weakness. Crit Care 19:448. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Homogenate | Human | Skeletal muscle |
| Soares 2015 PLoS One | 2015 | Soares JB, Gaviraghi A, Oliveira MF (2015) Mitochondrial physiology in the major arbovirus vector Aedes aegypti: substrate preferences and sexual differences define respiratory capacity and superoxide production. PLoS One 10:e0120600. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized tissue Isolated mitochondria | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Mourier 2015 J Cell Biol | 2015 | Mourier A, Motori E, Brandt T, Lagouge M, Atanassov I, Galinier A, Rappl G, Brodesser S, Hultenby K, Dieterich C, Larsson NG (2015) Mitofusin 2 is required to maintain mitochondrial coenzyme Q levels. J Cell Biol 208:429-42. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp Other combinations | Permeabilized cells Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart Fibroblast |
| Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways | 2014 | Gnaiger E (2014) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 4th ed. Mitochondr Physiol Network 19.12. Oroboros MiPNet Publications, Innsbruck:80 pp. — see 5th edition: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse | Heart Skeletal muscle Fibroblast |
| Baggio 2014 Nucleic Acids Res | 2014 | Baggio F, Bratic A, Mourier A, Kauppila TE, Tain LS, Kukat C, Habermann B, Partridge L, Larsson NG5 (2014) Drosophila melanogaster LRPPRC2 is involved in coordination of mitochondrial translation. Nucleic Acids Res 42:13920-38. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV Other combinations | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila Hexapods | |
| Pecina 2014 Biochim Biophys Acta Clinical | 2014 | Pecina P, Houstkova H, Mracek T, Pecinova A, Nuskova H.Tesarova M, Hansikova H, Janota J, Zemanc J, Houstek J (2014) Noninvasive diagnostics of mitochondrial disorders in isolated lymphocytes with high resolution respirometry. Biochim Biophys Acta Clinical 2:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2014.09.003 | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells Lymphocyte |
| Tretter 2014 Free Radic Biol Med | 2014 | Tretter L, Horvath G, Hölgyesi A, Essek F, Adam-Vizi V (2014) Enhanced hydrogen peroxide generation accompanies the beneficial bioenergetic effects of methylene blue in isolated brain mitochondria. Free Radic Biol Med 77:317-30. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Guinea pig | Nervous system |
| Ludzki 2014 Thesis | 2014 | Ludzki AC (2014) Palmitoyl-CoA inhibition of mitochondrial ADP sensitivity is attenuated by exercise training in human skeletal muscle. Master's Thesis 1-86. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue | Human Mouse | Skeletal muscle |
| Petruzzelli 2014 Cell Metab | 2014 | Petruzzelli M, Schweiger M, Schreiber R, Campos-Olivas R, Tsoli M, Allen J, Swarbrick M, Rose-John S, Rincon M, Robertson G, Zechner R, Wagner EF (2014) A switch from white to brown fat increases energy expenditure in cancer-associated cachexia. Cell Metab 20:433-47. | Gp | Mouse | Fat | ||
| Divakaruni 2014 Curr Protoc Toxicol | 2014 | Divakaruni AS, Rogers GW, Murphy AN (2014) Measuring mitochondrial function in permeabilized cells using the Seahorse XF Analyzer or a clark-type oxygen electrode. Curr Protoc Toxicol 60:25.2.1-25.2.16. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Permeabilized cells | Mouse | Skeletal muscle Other cell lines |
| Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque 2014 J Appl Physiol | 2014 | Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque JP, Salvador IC, Martins EL, Jardim-Messeder D, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Galina A, Carvalho DP (2014) Role of estrogen on skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in ovariectomized rats: a time course study in different fiber types. J Appl Physiol 116:779-89. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Skeletal muscle |
| Kupsch 2014 J Neural Transm | 2014 | Kupsch A, Schmidt W, Gizatullina Z, Debska-Vielhaber G, Voges J, Striggow F, Panther P, Schwegler H, Heinze HJ, Vielhaber S, Gellerich FN (2014) 6-Hydroxydopamine impairs mitochondrial function in the rat model of Parkinson's disease: respirometric, histological, and behavioral analyses. J Neural Transm 121:1245-57. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp | Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Nervous system |
| Enriquez 2014 Mol Syndromol | 2014 | Enriquez JA, Lenaz G (2014) Coenzyme Q and the respiratory chain: coenzyme Q pool and mitochondrial supercomplexes. Mol Syndromol 5:119-40. | N S CIV Gp | Isolated mitochondria | |||
| Chakraborty 2014 J Cardiovasc Dis | 2014 | Chakraborty M, Phillips ARJ, Macdonald J, Windsor JA, Hickey AJR (2014) Mitochondrial respiration in mononuclear cells and heart fibers in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Dis ISSN:2330-459. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Heart Blood cells |
| Clarke 2013 Int J Biochem Cell Biol | 2013 | Clarke KJ, Porter RK (2013) Uncoupling protein 1 dependent reactive oxygen species production by thymus mitochondria. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:81-9. | LEAK ET | N S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Islet cell;pancreas;thymus |
| Wredenberg 2013 PLoS Genet | 2013 | Wredenberg A, Lagouge M, Bratic A, Metodiev MD, Spåhr H, Mourier A, Freyer C, Ruzzenente B, Tain L, Grönke S, Baggio F, Kukat C, Kremmer E, Wibom R, Polosa PL, Habermann B, Partridge L, Park CB, Larsson NG (2013) MTERF3 regulates mitochondrial ribosome biogenesis in invertebrates and mammals. PLoS Genet 9:e1003178. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Tretter 2012 Free Radic Biol Med | 2012 | Tretter Laszlo, Adam-Vizi Vera (2012) High Ca2+ load promotes hydrogen peroxide generation via activation of α-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase in brain mitochondria. Free Radic Biol Med 53:2119-30. | Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Guinea pig | Nervous system | |
| Guillet 2011 FASEB J | 2011 | Guillet V, Gueguen N, Cartoni R, Chevrollier A, Desquiret V, Angebault C, Amati-Bonneau P, Procaccio V, Bonneau D, Martinou JC, Reynier P (2011) Bioenergetic defect associated with mKATP channel opening in a mouse model carrying a mitofusin 2 mutation. FASEB J 25:1618-27. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Bratic 2011 PLoS Genet | 2011 | Bratic A, Wredenberg A, Grönke S, Stewart JB, Mourier A, Ruzzenente B, Kukat C, Wibom R, Habermann B, Partridge L, Larsson NG (2011) The bicoid stability factor controls polyadenylation and expression of specific mitochondrial mRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet 7:e1002324. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS Other combinations | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila | |
| Pichaud 2010 J Exp Biol | 2010 | Pichaud N, Chatelain EH, Ballard JWO, Tanguay R, Morrow G, Blier PU (2010)Thermal sensitivity of mitochondrial metabolism in two distinct mitotypes of Drosophila simulans: Evaluation of mitochondrial plasticity. J Exp Biol 213:1665-75. | OXPHOS ET | N Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Drosophila | Skeletal muscle |
| Tahara 2009 Free Radic Biol Med | 2009 | Tahara EB, Navarete FD, Kowaltowski AJ (2009) Tissue-, substrate-, and site-specific characteristics of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radic Biol Med 46:1283-97. | LEAK ET OXPHOS | F N NS ROX S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Heart Skeletal muscle Nervous system Liver Kidney |
| Giulivi 2008 Biochem J | 2008 | Giulivi C, Ross-Inta C, Horton AA, Luckhart S (2008) Metabolic pathways in Anopheles stephensi mitochondria. Biochem J 415:309-16. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV Other combinations ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Human Rat Birds Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Gnaiger 2007 MitoPathways | 2007 | Gnaiger E ed (2007) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. 1st ed. Oroboros MiPNet Publications, Innsbruck:96 pp. ISBN 978-3-9502399-0-4. — see 5th edition: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways. | F N S Gp NS | ||||
| Vrbacky 2007 Biochim Biophys Acta | 2007 | Vrbacky M, Drahota Z, Mracek T, Vojtískova A, Jesina P, Stopka P, Houstek J (2007) Respiratory chain components involved in the glycerophosphate dehydrogenase-dependent ROS production by brown adipose tissue mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:989-97. | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Other mammals | Fat | |
| Ponsot 2005 J Cell Physiol | 2005 | Ponsot E, Zoll J, N'guessan B, Ribera F, Lampert E, Richard R, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R, Mettauer B (2005) Mitochondrial tissue specificity of substrates utilization in rat cardiac and skeletal muscles. J Cell Physiol 203:479-86. | OXPHOS | F N Gp | Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Heart Skeletal muscle |
| Rauchova 2005 Biochem Biophys Res Comm | 2005 | Rauchova H, Vrbacky M, Bergamini C, Fato R, Lenaz G, Houstek J, Drahota Z (2005) Inhibition of glycerophosphate-dependent H2O2 generation in brown fat mitochondria by idebenone. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 339:362-6. | S Gp Other combinations | ||||
| Chowdhury 2005 Biochem Biophys Res Comm | 2005 | Chowdhury SK, Gemin A, Singh G (2005) High activity of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and glycerophosphate-dependent ROS production in prostate cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 333:1139-45. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | Gp | Permeabilized cells | Human | Genital |
| Rauchova 2003 Acta Biochim Pol | 2003 | Rauchová H, Drahota Z, Rauch P, Fato R, Lenaz G (2003) Coenzyme Q releases the inhibitory effect of free fatty acids on mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase. Acta Biochim Pol 50:405-13. | N S Gp Other combinations | Isolated mitochondria | Other mammals | Fat | |
| Rasmussen 2001 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab | 2001 | Rasmussen UF, Rasmussen HN, Krustrup P, Quistorff B, Saltin B, Bangsbo J (2001) Aerobic metabolism of human quadriceps muscle: in vivo data parallel measurements on isolated mitochondria. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E301-7. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS | Isolated mitochondria | Human | Skeletal muscle |
| Villani 1997 Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | 1997 | Villani G, Attardi G (1997) In vivo control of respiration by cytochrome c oxidase in wild-type and mitochondrial DNA mutation-carrying human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:1166-71. | ROUTINE ET OXPHOS | N S Gp ROX | Intact cells Permeabilized cells | Human | Fibroblast |
| Moyes 1989 J Exp Biol | 1989 | Moyes CD, Buck LT, Hochachka PW, Suarez RK (1989) Oxidative properties of carp red and white muscle. J Exp Biol 143:321-31. | OXPHOS | F N Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Skeletal muscle | |
| Klingenberg 1970 Eur J Biochem | 1970 | Klingenberg M (1970) Localization of the glycerol-phosphate dehydrogenase in the outer phase of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Eur J Biochem 13:247-52. | ET | Gp | Isolated mitochondria |
- »Abstracts: Gp-pathway control state
Abstracts: Gp-pathway control state
Sort in ascending/descending order by a click on one of the small symbols in squares below.
| Year | Reference | Coupling | Pathway | Preparation | Organism | Tissue;cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timon-Gomez 2023 EUROMIT2023 Bologna | 2023 | Timon-Gomez A, Cardoso L, Baglivo E, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (2023) Mitochondrial injury in warm ischemia studied by high-resolution respirometry. EUROMIT2023 International Conference on Mitochondrial Pathology. | OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp | Homogenate Isolated mitochondria Intact cells | Human Mouse | Heart Nervous system HEK |
| Cecatto 2023 BPS2023 San Diego | 2023 | Cecatto C, Schmitt Sabine, Cardoso L, Videja M, Dambrova M, Makrecka-Kuka M, Liepinsh E, Gnaiger E (2023) Contribution of fatty acid oxidation to respiratory control in brain mitochondria. 67th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society. | OXPHOS | F N Gp NS | Permeabilized tissue Homogenate | Mouse | Heart Nervous system Kidney |
| Irving 2022 Abstract Bioblast | 2022 | 7.4. «5 min» Irving Brian A, Stampley J, Quiriarte H, Wigger Z, Stephens J, Soto P, Allerton TA (2022) Impact of nitric oxide promotors on mitochondrial bioenergetics in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease. Bioblast 2022: BEC Inaugural Conference. In: https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0001 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N Gp NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue Homogenate | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Molina 2022 Abstract Bioblast | 2022 | 3.2. «10+5» Heimler SR, Phang HJ, Bergstrom J, Mahapatra G, Dozier S, Gnaiger E, Molina Anthony JA (2022) Platelet bioenergetics are associated with resting metabolic rate and exercise capacity in older women. Bioblast 2022: BEC Inaugural Conference. In: https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2022-0001 »Bioenergetics Communications« | OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells |
| Sumbalova 2019a MiP2019 | 2019 | Platelet mitochondrial function, coenzyme Q10, and oxidative stress in patients with chronic kidney diseases. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells | Human | Platelet |
| Sumbalova 2019b MiP2019 | 2019 | The decline of mitochondrial respiration in isolated platelets after short-term storage. | LEAK OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells | Human | Platelet |
| Garcia 2019 MiPschool Coimbra | 2019 | Functional interactions between the Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and a xenotopically expressed alternative oxidase. | LEAK OXPHOS | N Gp | Drosophila | ||
| Komlodi 2018 AussieMit | 2018 | Komlodi T, Hunger M, Moore AL, Gnaiger E (2018) Electron transfer at the Q-junction: new perspectives from combined measurement of mitochondrial O2 flux, H2O2 flux, and coenzyme Q redox state. AussieMit 2018 Melbourne AU. | LEAK OXPHOS | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Chang 2018 Life Sciences Meeting 2018 Innsbruck AT | 2018 | pH dependence of mitochondrial respiration and H2O2 production in oral cancer cells – a pilot study. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells | Human | HEK Kidney |
| Doerrier 2018 ESCI2018 | 2018 | High-resolution respirometry, two techniques combined in one to explore mitochondrial function in health and disease | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp ROX CIV | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | Human Mouse | Heart Skeletal muscle Nervous system Blood cells HEK |
| Komlodi 2018 EBEC2018 | 2018 | Electron supply to the Q-junction: assessment of mitochondrial respiration, H2O2 flux and the redox state of the Q-pool. | LEAK OXPHOS | S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Doerrier 2018 EBEC2018 | 2018 | Respiratory mapping of mitochondrial pathways for establishing a database of mitochondrial physiology. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | Human Mouse | Heart Nervous system Blood cells HEK Platelet |
| Gnaiger 2018 MiP2018 | 2018 | Mitochondrial respiratory control by fuel substrates and specific inhibitors of respiratory enzymes: Building blocks of mitochondrial physiology Part 2. | OXPHOS | N F S Gp DQ CIV NS Other combinations | |||
| Gnaiger 2018 MiPschool Tromso A1 | 2018 | Mitochondrial states and rates: 1. Electron transfer pathways and respiratory control. 2. Coupling control. | LEAK ET OXPHOS | F N S Gp DQ CIV NS Other combinations | |||
| Gainutdinov 2017 MITOEAGLE Obergurgl | 2017 | Different ways of reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation by brain mitochondria. | N S Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse Rat | Nervous system | |
| Wu 2017 FASEB J | 2017 | Effects of eccentric and concentric cycling exercise regimens on hypoxia-mediated mitochondrial bioenergetics of platelets in sedentary males. | F N S Gp | Human | Blood cells Platelet | ||
| Doerrier 2017 MiPschool C2 | 2017 | Substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocols – fundamental principles. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV | Permeabilized cells Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | Human Mouse | Heart Nervous system HEK |
| Gnaiger 2017 MiPschool A4 | 2017 | Respiratory pathway control in mitochondrial core energy metabolism: from bioenergetics to mitochondrial physiology. | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Isolated mitochondria | |||
| Ukropec 2017 MITOEAGLE Obergurgl | 2017 | Could functional state of muscle mitochondria reflect exercise-induced changes in insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance and cognitive performance in individuals with mild cognitive impairment? | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS | Permeabilized cells | Skeletal muscle | |
| Komlodi 2017 MiPschool Obergurgl | 2017 | Electron pressure exerted by convergent succinate- and glycerophosphate-pathways to the Q-junction regulate reversed electron transfer to Complex I and H2O2 production. | LEAK OXPHOS | N S Gp Other combinations ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Nervous system |
| Collins 2017 MiPschool Obergurgl | 2017 | The effects of a Mediterranean versus Western diet on nonhuman primate skeletal muscle bioenergetics. | OXPHOS | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Intact cells | ||
| Doerrier 2017 Abstract MitoEAGLE Barcelona | 2017 | SUIT reference protocol for comparative mitochondrial physiology. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV | Permeabilized cells Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | Human Mouse | Heart Nervous system HEK |
| Sobotka 2017 Abstract MITOEAGLE Barcelona | 2017 | The effect of 24 weeks of high-fat and high-cholesterol diet on rat liver mitochondria. Sobotka_Presentation | OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Liver |
| Sumbalova 2016b Abstract MitoFit Science Camp 2016 | 2016 | Human blood cells: isolation and HRR. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Intact cells | Human | Blood cells Lymphocyte Platelet |
| Lamberti 2016 Abstract MitoFit Science Camp 2016 | 2016 | Development of a reference sample for HRR. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Human | Kidney HEK | |
| Doerrier 2016 Abstract MitoFit Science Camp 2016 | 2016 | Development of a SUIT reference protocol for OXPHOS analysis by high-resolution respirometry. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Isolated mitochondria | Human Mouse | Heart Blood cells HEK Platelet |
| Sobotka 2016 Abstract IOC116 | 2016 | Sobotka O, Kucera Otto, Stankova P, Endlicher R, Nozickova K, Banni A, Cervinkova Z (2016) Mitochondrial respiration in fatty liver. Mitochondr Physiol Network 21.11 | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV NS Other combinations ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Rat | Liver |
| Doerrier 2016b Abstract Mito Xmas Meeting Innsbruck | 2016 | Searching for specific targets of ischemic damage of cardiac mitochondria using O2k-Fluorometry. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Isolated mitochondria | Mouse | Heart |
| Pecina 2014 Abstract MiP2014 | 2014 | Manifestation of mitochondrial disorders of nuclear origin in lymphocytes. | OXPHOS | N S Gp CIV | Permeabilized cells | Human | Blood cells Lymphocyte |
| Darveau 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Darveau CA, Teulier L, Crevier J, Weber JM (2013) Diversity and evolution of mitochondrial metabolism: Proline as a metabolic reward for pollinators. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | OXPHOS | N S Gp NS Other combinations | Permeabilized tissue | Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Pecina 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Pecina P, Houšťková H, Mráček T, Pecinová A, Nůsková H, Tesařová M, Hansíková H, Janota J, Zeman J, Houštěk J (2013) The use of lymphocytes for diagnostics of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation disorders. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp NS Other combinations ROX | Permeabilized cells Homogenate | Human | Blood cells Lymphocyte |
| Cavalcanti de Albuquerque 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Cavalcanti de Albuquerque JP, Salvador IC, Martins EG, Jardim-Messeder D; Werneck de Castro JPS; Carvalho DP; Galina A (2013) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in ovariectomized rats: A time course study and the role of estrogen replacement. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp NS ROX | Intact organism Permeabilized tissue | Rat | Skeletal muscle |
| Shabalina 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Shabalina IG, Petrovic N, Kalinovich AV, Cannon B, Nedergaard J (2013) Comparative study of brown and white adipose tissue mitochondria in mice upon cold acclimation. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | OXPHOS ET | Gp | Isolated mitochondria | Fat | |
| Pichaud 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Pichaud N, Blier PU(2013) Importance of mitochondrial haplotypes in the expression of metabolic phenotypes under different conditions. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | LEAK OXPHOS ET | N S Gp CIV NS ROX | Permeabilized tissue | Drosophila Hexapods | Skeletal muscle |
| Oliveira MF 2013 Abstract MiP2013 | 2013 | Oliveira MF (2013) Comparative mitochondrial physiology in blood feeding insect vectors and parasites. Mitochondr Physiol Network 18.08. | LEAK ROUTINE OXPHOS ET | F N S Gp CIV ROX | Intact organism Intact organ Permeabilized cells Permeabilized tissue Homogenate Intact cells | Human Drosophila Hexapods Other invertebrates | Skeletal muscle Neuroblastoma |
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
SUIT state,
Recommended
MitoPedia topics:
EAGLE