Template:SUIT-006 O2 ce-pce D029
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ce1 | ROUTINE | ce1
| ||
| 1Dig | REN | ce1;1Dig
|
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
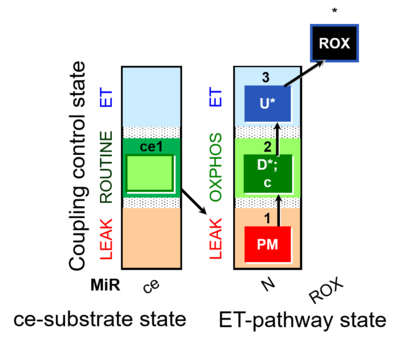
| 1PM | PML | N | CI | PML or PM_L: Pyruvate & Malate, N-LEAK respiration, NL
NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). Template:SUIT L n |
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D
NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c
NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM (cytochrome c control efficiency). Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in the preceding state without added c due to loss of cytochrome c. Typically, cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step (OXPHOS capacity P with saturating [ADP]). |
| 3U | PME | N | CI | 1PM;2D;3U
NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity E (noncoupled ET-state). Test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity P by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET capacity E in mt-preparations: E-P control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. In living cells: E-R control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. |
| 4Ama | ROX | Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of CIII). Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration (mt). |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary