Description
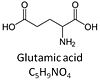
Glutamic acid, C5H9NO4, is an amino acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly as the anion glutamate-, G, with pKa1 = 2.1, pKa2 = 4.07 and pKa3 = 9.47. Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the glutamate-aspartate carrier and reacts with oxaloacetate in the transaminase reaction to form aspartate and oxoglutarate. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by glutamate dehydrogenase to α-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate), representing the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state. Ammonia (the byproduct of the reaction) passes freely through the mitochondrial membrane.
Abbreviation: G
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Application in HRR
- G: Glutamate (L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate; C₅H₈NNaO₄ · xH₂O), Sigma-Aldrich: G1626, store at RT, CAS: 142-47-2, M = 169.1 g·mol-1
- Preparation of 2 M stock solution (dissolved in H2O)
- Weigh 1.691 g L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate.
- Add 4 mL H2O.
- Check pH and adjust to 7.0 if necessary with 5 M KOH (usually the pH is 7 without any adjustment);
- Transfer to a 5 mL volumetric glass flask, adjust final volume to 5 mL and divide into 0.5 mL portions.
- Store at -20 °C.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (2-mL O2k-chamber): 10 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Titration volume (0.5-mL O2k-chamber): 2.5 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe
- Final concentration: 10 mM.
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite