Gnaiger 2015 Scand J Med Sci Sports
| Gnaiger E, Boushel R, Søndergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Damsgaard R, Hagen C, Díez-Sánchez C, Ara I, Wright-Paradis C, Schrauwen P, Hesselink M, Calbet JAL, Christiansen M, Helge JW, Saltin B (2015) Mitochondrial coupling and capacity of oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle of Inuit and caucasians in the arctic winter. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25 (Suppl 4):126–34. |
» PMID: 26589126 Open Access »![]()
Gnaiger E, Boushel R, Soendergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Damsgaard R, Hagen C, Diez-Sanchez C, Ara I, Wright-Paradis C, Schrauwen P, Hesselink M, Calbet JA, Christiansen M, Helge JW, Saltin B (2015) Scand J Med Sci Sports
Abstract:  O2k-in brief
O2k-in brief
During evolution, mtDNA haplogroups of arctic populations may have been selected for lower coupling of mitochondrial respiration to ATP production in favor of higher heat production. We show that mitochondrial coupling in skeletal muscle of traditional and westernized Inuit habituating northern Greenland is identical to Danes of western Europe haplogroups. Biochemical coupling efficiency was preserved across variations in diet, muscle fibre type and uncoupling protein-3 content. Mitochondrial phenotype displayed plasticity in relation to lifestyle and environment. Untrained Inuit and Danes had identical capacities to oxidize fat substrate in arm muscle, which increased in Danes during the 42 days of acclimation to exercise, approaching the higher level of the Inuit hunters. A common pattern emerges of mitochondrial acclimatization and evolutionary adaptation in humans at high latitude and high altitude where economy of locomotion may be optimized by preservation of biochemical coupling efficiency at modest mitochondrial density, when submaximum performance is uncoupled from VO2max and maximum capacities of oxidative phosphorylation. • Keywords: BMI, VO2max • Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E • O2k-Network Lab: AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E, AT Innsbruck Oroboros, CA Vancouver Boushel RC, NL Maastricht Schrauwen P, DK Copenhagen Christiansen M, ES CN Las Palmas Calbet JA
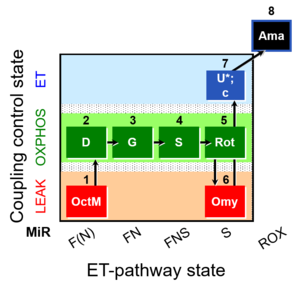
SUIT protocol
Greenland expedition CMRC: science and adventure
MitoEAGLE VO2max/BME data base
- Human vastus lateralis
- 8 females & 8 males
- 31 years
- Active; Danes, baseline control in Copenhagen
- H = 1.75 m
- M = 74.5 kg
- BME = 1.19
- BMI = 24.3 kg·m-2
- VO2max/BM = 48.0 mL·min-1·kg-1
- Permeabilized muscle fibres; 30 °C; GMSP; mw; conversions: Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol
- JO2,P(NS) = 90.5 µmol·s-1·kg-1 wet muscle mass (37 °C)
Bengt Saltin - a Gentle Scientist
Additional references
- Marconi C, Marzorati M, Cerretelli P (2006) Work capacity of permanent residents of high altitude. High Alt Med Biol 7:105-115. - »Bioblast link«
- Tam E, Bruseghini P, Calabria E, Sacco LD, Doria C, Grassi B, Pietrangelo T, Pogliaghi S, Reggiani C, Salvadego D, Schena F, Toniolo L, Verratti V, Vernillo G, Capelli C (2015) Gokyo Khumbu/Ama Dablam Trek 2012: effects of physical training and high-altitude exposure on oxidative metabolism, muscle composition, and metabolic cost of walking in women. Eur J Appl Physiol. - »Bioblast link«
O2k-brief
MitoFit news 2015#18
- 2015-11-25: Performance tests on skeletal muscle mitochondria of the Inuit haplogroup reveal fitness information beyond the uncoupling hypothesis for adaptations to the arctic climate. » MitoFit news - a contribution to K-Regio MitoFit.
References: BME and VO2max
- » VO2max
| Reference | |
|---|---|
| Bakkman 2007 ActaPhysiol | Bakkman L, Sahlin K, Holmberg HC, Tonkonogi M (2007) Quantitative and qualitative adaptation of human skeletal muscle mitochondria to hypoxic compared with normoxic training at the same relative work rate. Acta Physiol (Oxford) 190:243–51. |
| Boushel 2007 Diabetologia | Boushel RC, Gnaiger E, Schjerling P, Skovbro M, Kraunsoee R, Dela F (2007) Patients with Type 2 diabetes have normal mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 50:790-6. |
| Chambers 2020 J Appl Physiol (1985) | Chambers TL, Burnett TR, Raue U, Lee GA, Finch WH, Graham BM, Trappe TA, Trappe S (2020) Skeletal muscle size, function, and adiposity with lifelong aerobic exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 128:368–78. |
| Daussin 2008 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol | Daussin FN, Zoll J, Dufour SP, Ponsot E, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Doutreleau S, Mettauer B, Piquard F, Geny B, Richard R (2008) Effect of interval versus continuous training on cardiorespiratory and mitochondrial functions: relationship to aerobic performance improvements in sedentary subjects. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R264-72. |
| Garnier 2005 FASEB J | Garnier A, Fortin D, Zoll J, N'Guessan B, Mettauer B, Lampert E, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R (2005) Coordinated changes in mitochondrial function and biogenesis in healthy and diseased human skeletal muscle. FASEB J 19:43-52. |
| Gnaiger 2015 Scand J Med Sci Sports | Gnaiger E, Boushel R, Søndergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Damsgaard R, Hagen C, Díez-Sánchez C, Ara I, Wright-Paradis C, Schrauwen P, Hesselink M, Calbet JAL, Christiansen M, Helge JW, Saltin B (2015) Mitochondrial coupling and capacity of oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle of Inuit and caucasians in the arctic winter. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12612 |
| Gnaiger 2019 MiP2019 | OXPHOS capacity in human muscle tissue and body mass excess – the MitoEAGLE mission towards an integrative database (Version 6; 2020-01-12). |
| Loe 2013 PLOS ONE | Loe H, Rognmo Ø, Saltin B, Wisløff U (2013) Aerobic capacity reference data in 3816 healthy men and women 20-90 years. PLOS ONE 8:e64319. |
| Mettauer 2001 J Am Coll Cardiol | Mettauer B, Zoll J, Sanchez H, Lampert E, Ribera F, Veksler V, Bigard X, Mateo P, Epailly E, Lonsdorfer J, Ventura-Clapier R (2001) Oxidative capacity of skeletal muscle in heart failure patients versus sedentary or active control subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 38:947-54. |
| Mogensen 2006 J Physiol | Mogensen M, Bagger M, Pedersen PK, Fernström M, Sahlin K (2006) Cycling efficiency in humans is related to low UCP3 content and to type I fibres but not to mitochondrial efficiency. J Physiol 571:669-81. |
| N'Guessan 2004 Mol Cell Biochem | N'Guessan B, Zoll J, Ribera F, Ponsot E, Lampert E, Ventura-Clapier R, Veksler V, Mettauer B (2004) Evaluation of quantitative and qualitative aspects of mitochondrial function in human skeletal and cardiac muscles. Mol Cell Biochem 256-257:267-80. |
| Pesta 2011 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol | Pesta D, Hoppel F, Macek C, Messner H, Faulhaber M, Kobel C, Parson W, Burtscher M, Schocke M, Gnaiger E (2011) Similar qualitative and quantitative changes of mitochondrial respiration following strength and endurance training in normoxia and hypoxia in sedentary humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1078–87. |
| Ponsot 2006 J Appl Physiol (1985) | Ponsot E, Dufour SP, Zoll J, Doutrelau S, N'Guessan B, Geny B, Hoppeler H, Lampert E, Mettauer B, Ventura-Clapier R, Richard R (2006) Exercise training in normobaric hypoxia in endurance runners. II. Improvement of mitochondrial properties in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 100:1249-57. |
| Pribis 2010 Nutrients | Pribis P, Burtnack CA, McKenzie SO, Thayer J (2010) Trends in body fat, body mass index and physical fitness among male and female college students. Nutrients 2:1075-85. |
| Raboel 2009 Diabetes Obes Metab | Raboel R, Hojberg PM, Almdal T, Boushel RC, Haugaard SB, Madsbad S, Dela F (2009) Improved glycaemic control decreases inner mitochondrial membrane leak in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:355-60. |
| Rasmussen 2001 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab | Rasmussen UF, Rasmussen HN, Krustrup P, Quistorff B, Saltin B, Bangsbo J (2001) Aerobic metabolism of human quadriceps muscle: in vivo data parallel measurements on isolated mitochondria. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E301-7. |
| Rasmussen 2003 Eur J Physiol | Rasmussen UF, Krustrup P, Kjaer M, Rasmussen HN (2003) Human skeletal muscle mitochondrial metabolism in youth and senescence: no signs of functional changes in ATP formation and mitochondrial oxidative capacity. Pflugers Arch – Eur J Physiol 446:270-78. |
| Zoll 2002 J Physiol | Zoll J, Sanchez H, N'Guessan B, Ribera F, Lampert E, Bigard X, Surrurier B, Fortin D, Geny B, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R, Mettauer B (2002) Physical activity changes the regulation of mitochondrial respiration in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 543:191-200. |
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, mt-Biogenesis;mt-density, mtDNA;mt-genetics, Comparative MiP;environmental MiP, Gender, Exercise physiology;nutrition;life style
Stress:Temperature Organism: Human Tissue;cell: Skeletal muscle Preparation: Permeabilized tissue Enzyme: Marker enzyme, TCA cycle and matrix dehydrogenases Regulation: Coupling efficiency;uncoupling, Cyt c Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET Pathway: F, N, S, ROX HRR: Oxygraph-2k, O2k-Protocol
MitoFitPublication, VO2max, BMI, BME, 1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot;6Omy;7U-, SUIT-016, SUIT-016 O2 pfi D044, MitoEAGLE BME