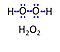From Bioblast
 |
PB-Module |
Description
The PB-Module has been developed for conducting measurements of PhotoBiology, including photosynthesis. It consists of the PB Light Source and electronic components which are an integral part of the NextGen-O2k. Measurements are recorded and evaluated with the DatLab 8 software.
Reference: Product details and purchase information
The PB-Module of the NextGen-O2k and O2k-J and higher
Additional resources
Support
- Supported by project NextGen-O2k which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 859770.
MitoPedia: NextGen-O2k
| Term | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 or dihydrogen dioxide, is one of several reactive oxygen intermediates generally referred to as reactive oxygen species (ROS). It is formed in various enzyme-catalyzed reactions (e.g., superoxide dismutase) with the potential to damage cellular molecules and structures. H2O2 is dismutated by catalase to water and oxygen. H2O2 is produced as a signaling molecule in aerobic metabolism and passes membranes more easily compared to other ROS. |
| Light-enhanced dark respiration | LEDR | Light-enhanced dark respiration LEDR is a sharp (negative) maximum of dark respiration in plants in response to illumination, measured immediately after switching off the light. LEDR is supported by respiratory substrates produced during photosynthesis and closely reflects light-enhanced photorespiration (Xue et al 1996). Based on this assumption, the total photosynthetic oxygen flux TP is calculated as the sum of the measured net photosynthetic oxygen flux NP plus the absolute value of LEDR. |
| Mitochondrial membrane potential | mtMP, ΔΨp+, ΔelFep+ [V] | The mitochondrial membrane potential difference, mtMP or ΔΨp+ = ΔelFep+, is the electric part of the protonmotive force, Δp = ΔmFeH+.
|
| NADH-Module | The NADH-Module, is a component of the Oroboros NextGen-O2k for simultaneous measurement of oxygen consumption and NAD(P)H autofluorescence. NAD(P)H autofluorescence is used to evaluate the redox state of the NAD(P)H-pool. The NADH-Module incorporates an UV light and NADH-Sensors which include a photodiode and specific filters. | |
| NADH-Sensor | The NADH-Sensor has been developed as a part of the NADH-Module for simultaneous monitoring of oxygen consumption and NADH redox state. The NADH-Sensor is composed of a photodiode and equipped with three supergel R370 Italian blue filters (Rosco, US). | |
| NextGen-O2k Technical developments | ||
| Oroboros NextGen-O2k | NextGen-O2k |
|
| Oxygen kinetics | Oxygen kinetics describes the dependence of respiration of isolated mitochondria or cells on oxygen partial pressure. Frequently, a strictly hyperbolic kinetics is observed, with two parameters, the oxygen pressure at half-maximum flux, p50, and maximum flux, Jmax. The p50 is in the range of 0.2 to 0.8 kPa for cytochrome c oxidase, isolated mitochondria and small cells, strongly dependent on Jmax and coupling state. | |
| PB Light Source | PBLS | The PhotoBiology Light Source (PBLS) has been designed as a part of the PB-Module to provide with an external source of light. This enables experiments for evaluating the production of O2 in the presence of light. The PBLS consists of one LED and one photodiode mounted on the PBLS head protected by a PMMA plastic cover. Three pairs of PBLS (white, blue, and red) are provided with the PB-Module. The light intensity can be regulated from 0 to 2750 µmol·s-1·m-2 (red PBLS), from 0 to 3000 µmol·s-1·m-2 (blue PBLS), from 0 to 3500 µmol·s-1·m-2 (white PBLS). An integrated photodiode provides real-time measurement of the light intensity allowing for continuous adjustment to the desired value. |
| PB-Module | The PB-Module has been developed for conducting measurements of PhotoBiology, including photosynthesis. It consists of the PB Light Source and electronic components which are an integral part of the Oroboros. Measurements are recorded and evaluated with the DatLab 8 software. | |
| PhotoBiology | PB | PhotoBiology is the science of the effect of light on biological processes. This includes photosynthesis, photochemistry, photophysics, photomorphogenesis, vision, bioluminescence, circadian rhythms and photodynamic therapy. Phototoxicity results from non-ionizing radiation (i.e. ultraviolet, visible and infrared radiation). Non-ionizing radiation is any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum (photon energy below 10 eV) to completely remove an electron from an atom or molecule. When photons interact with molecules, the molecules can absorb the photon energy and become excited, reacting with surrounding molecules and stimulating "photochemical" and "photophysical" changes. Respiration may be affected by light during photosynthesis or in dark respiration, with the transient response of light-enhanced dark respiration. |
| Photodecomposition | PD | Photodecomposition or photodegradation is the process of decay of organic material induced by increasing light intensity. Under aerobic conditions, the enhancement of photodecomposition by light intensity can be quantified by oxygen consumption in a controlled light regime. |
| Photosynthesis | PS | Photosynthesis is the process that converts light energy into chemical energy which is subsequently transformed to the physiological energy demand. Photosynthesis has a light-dependent and light-independent (dark) phase. In plants, algae, and cynobacteria, light energy is absorbed during the light phase by the pigment chlorophyll and used to split water and generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reducing power - nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), with the net production of O2 as a waste product. During the dark phase ATP and NADPH are used to synthesize carbohydrates from CO2 through the metabolic pathway called Calvin-Benson cycle. Oxygenic photosynthesis is responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen concentration of the Earth’s atmosphere. In bacteria such as cyanobacteria, photosynthesis involves the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells (plants and algae), photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts. |
| Q-Module | Q-Module | The Q-Module, developed for measuring the Q redox state and cyclic voltammetry, is supported by the Oroboros NextGen-O2k and consists of the Q-Sensor, integrated electronic components, and the DatLab software. |
| Q-Sensor | The Q-Sensor has been designed as a part of the Q-Module for measurements with cyclic voltammetry and voltammetry, allowing for analysis of the Q redox state. The Q-Stopper with the reference electrode is called Q-Sensor, which is plugged in the NextGen-O2k. A three-electrode system is used to detect the Q redox state. Two of the three electrodes (glassy carbon and platinum electrode) are built into the Q-Stopper, while the reference electrode is removable (Reference-Electrode\2.4 mm). |
Expand
- Bioblast links: PhotoBiology and photosynthesis - >>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
MitoPedia:
Oroboros hardware,
O2k-Respirometry
Labels:
MitoPedia:NextGen-O2k