Difference between revisions of "Template:SUIT-016"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Steps and respiratory states == | == Steps and respiratory states == | ||
[[File:1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot;6Omy;7U-.png|300px]] | [[File:1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot;6Omy;7U-.png|300px]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2D | | 2D | ||
| [[ | | [[OctM]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state| F(N)]] | | [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state| F(N)]] | ||
| FAO | | FAO | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3G | | 3G | ||
| [[ | | [[OctGM]]c<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state| F(N)]] | | [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state| F(N)]] | ||
| CETF&I | | CETF&I | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4S | | 4S | ||
| [[ | | [[OctGMS]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[FNS]] | | [[FNS]] | ||
| CETF&CI&II | | CETF&CI&II | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 22 January 2019
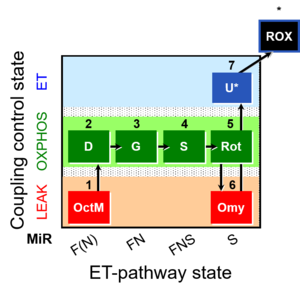
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1OctM | OctML | F(N) | FAO | OctML or OctM_L: Octanoylcarnitine & low malate, N-LEAK respiration, NL
Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. Low concentration of malate, typically 0.1 mM, does not saturate the N-pathway; but saturates the F-pathway. Template:SUIT L n |
| 2D | OctMP | F(N) | FAO | 1OCtM;2D
Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. Low concentration of malate, typically 0.1 mM, does not saturate the N-pathway; but saturates the F-pathway. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 3G | OctGMcP | F(N) | CETF&I | 1OCtM;2D;3G
Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. & NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 4S | OctGMSP | FNS | CETF&CI&II | 1OCtM;2D;3G;4S
Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of type N substrates & succinate, with convergent electron flow in the NS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function. Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 5Rot | SP | S | CII | 1OCtM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot
Succinate pathway control state (S-pathway) after inhibiting CI with rotenone, which also inhibits the F-pathway. Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 6Omy | SL | S | CII | 1OCtM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot;6Omy
Template:SUIT L n Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). |
| 7U | SE | S | CII | 1OCtM;2D;3G;4S;5Rot;6Omy;7U
Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity E (noncoupled ET-state). Test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity P by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET capacity E in mt-preparations: E-P control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. In living cells: E-R control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E.
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary