Template:SUIT-009 O2 pce D016
From Bioblast
Revision as of 14:13, 23 January 2019 by Komlodi Timea (talk | contribs) (Created page with "right|190px|link=http://www.bioblast.at/index.php/MitoPedia:_SUIT |MitoPedia: SUIT 300px {{Template:ROUTINE Dig}} {...")
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ce1 | ROUTINE | ce1
| ||
| 1Dig | Dig | ce1;1Dig
|
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
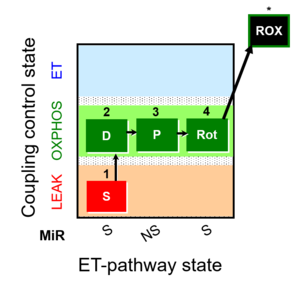
| 1S | SL | S | CII | SL or S_L: Succinate, S-LEAK respiration, SL
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Template:SUIT L n |
| 2D | SP | S | CII | 1S;2D
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 3P | NSP | NS | CI&II | 1S;2D;3P
NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). & Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of type N substrates & succinate, with convergent electron flow in the NS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. |
| 4Rot | SP | S | CII | 1S;2D;3P;4Rot
Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q). OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. Succinate pathway control state (S-pathway) after inhibiting CI with rotenone, which also inhibits the F-pathway.
|
| 6Ama | ROX | Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of CIII). Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration (mt). |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary