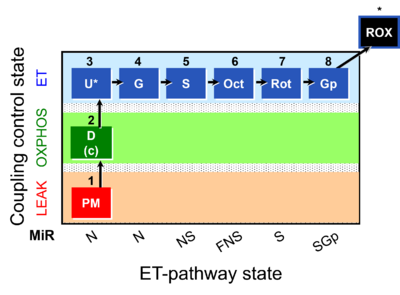
Template:SUIT-001
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | Pathway to Q |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PM(L) | N | CI |
| 2D | PM(P) | N | CI |
| 2c | PM(P)c | N | CI |
| 3U | PM(E) | N | CI |
| 4G | PGM(E) | N | CI |
| 5S | PGMS(E) | NS | CI&II |
| 6Oct | OctPGMS(E) | FNS | FAO&CI&II |
| 7Rot | S(E) | S | CII |
| 8Gp | SGp(E) | SGp | CII&GpDH |
| 9Ama | ROX | ROX | |
| 10Tm | Tm(E) | CIV | CIV |
| 11Azd | ROX | ROX |
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex entry into Q-junction | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GM | GML | N | CI | GML or GM_L: N-LEAK respiration, NL
NADH-linked substrates glutamate & malate (type N; CI-linked pathway to Q). Non-phosphorylating resting state (LEAK state); Ln in the absence of ADP, ATP, AMP (no adenylates). |
| 2D | GMP | N | CI | GMP or GM_P: N-OXPHOS capacity, NP
OXPHOS capacity, P (with saturating [ADP]), with NADH-linked substrates glutamate&malate. |
| D(c) | GMcP | N | CI | GMcP or GMc_P: Cytochrome c test for quality control
Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM. Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in state GMP due to loss of cytochrome c (P, OXPHOS capacity with type N substrates). Cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step. |
| 3S | GMSP | NS | CI&II | GMSP or GMS_P: NS-OXPHOS capacity, NSP
Respiratory stimulation by further addition of succinate, S, to type N substrates, with convergent electron flow in the NS-pathway (CI&II-linked pathway to the Q-junction) for reconstitution of TCA cycle function, in the coupled state as an estimate of OXPHOS-capacity, P. |
| 4U | GMSE | NS | CI&II | GMSE or GMS_E: NS-ET capacity, NSE
Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity (noncoupled ET-state), as a test for limitation of OXPHOS-capacity by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET-capacity, E. |
| 5Rot | SE | S | CII | SE or S_E: S-ET capacity
S-pathway ET-capacity after blocking CI with rotenone. |
| 6Ama | ROX | ROX: residual oxygen consumption
Rox is due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of Antimycin A (inhibitor of CIII). Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration (mt). |