Lemieux 2011 Int J Biochem Cell Biol
| Lemieux H, Semsroth S, Antretter H, Höfer D, Gnaiger E (2011) Mitochondrial respiratory control and early defects of oxidative phosphorylation in the failing human heart. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1729–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.08.008 |
» PMID: 21871578 » ![]()
Lemieux H, Semsroth S, Antretter H, Hoefer D, Gnaiger Erich (2011) Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Abstract:  O2k-in brief
O2k-in brief
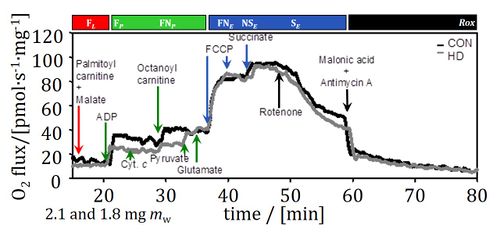
Heart failure is a consequence of progressive deterioration of cardiac performance. Little is known about the role of impaired oxidative phosphorylation in the progression of the disease, since previous studies of mitochondrial injuries are restricted to end-stage chronic heart failure. The present study aimed at evaluating the involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of human heart failure. We measured the control of oxidative phosphorylation with high-resolution respirometry in permeabilized myocardial fibres from donor hearts (controls), and patients with no or mild heart failure but presenting with heart disease, or chronic heart failure due to dilated or ischemic cardiomyopathy. The capacity of the phosphorylation system exerted a strong limitation on oxidative phosphorylation in the human heart, estimated at 121 pmol O2•s-1•mg-1 in the healthy left ventricle. In heart disease, a specific defect of the phosphorylation system, Complex I-linked respiration, and mass-specific fatty acid oxidation were identified. These early defects were also significant in chronic heart failure, where the capacities of the oxidative phosphorylation and Electron transfer-pathway per cardiac tissue mass were decreased with all tested substrate combinations, suggesting a decline of mitochondrial density. Oxidative phosphorylation and electron transfer-pathway capacities were higher in ventricles compared to atria, but the impaired mitochondrial quality was identical in the four cardiac chambers of chronic heart failure patients. Coupling was preserved in heart disease and chronic heart failure, in contrast to the mitochondrial dysfunction observed after prolonged cold storage of cardiac tissue. Mitochondrial defects in the phosphorylation system, Complex I respiration and mass-specific fatty acid oxidation occurred early in the development of heart failure. Targeting these mitochondrial injuries with metabolic therapy may offer a promising approach to delay the progression of heart disease. • Keywords: Oxidative phosphorylation, Mitochondrial respiratory control, Human heart disease and heart failure, Permeabilized cardiac fibres, Cold storage, High-resolution respirometry
• O2k-Network Lab: AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E, AT Innsbruck Oroboros, CA Edmonton Lemieux H
O2k-brief
SUIT protocols
O2k-Publications
- Increased OXPHOS capacity after cold preservation of the human heart – a paradox resolved by a dyscoupling mechanism.
- Human heart failure: mtDNA versus CS and PGC-1a pathway - PGC-1alpha
- Tissue storage
Review
Cited by
- 78 articles in PubMed (2024-04-17) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21871578/
- Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002
- Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. doi:10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1.
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, mt-Biogenesis;mt-density, mt-Medicine, Patients
Pathology: Cardiovascular
Stress:Ischemia-reperfusion
Organism: Human
Tissue;cell: Heart
Preparation: Permeabilized tissue
Enzyme: Marker enzyme
Regulation: Coupling efficiency;uncoupling, Cyt c, Fatty acid
Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET
Pathway: F, N, S, CIV, NS, ROX
HRR: Oxygraph-2k, O2k-Protocol
1PM;2D;3G;4U;5S;6Rot-, 1PalM;2D;3Oct;4P;5G;6U;7S;8Rot-, SUIT-019, SUIT-019 O2 pfi D045, O2k-brief, BEC 2020.1, BEC 2020.2