Difference between revisions of "SUIT-015"
From Bioblast
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
:::+ FNS OXPHOS capacity comprises the most important pathways in many cell types and thus provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity. | :::+ FNS OXPHOS capacity comprises the most important pathways in many cell types and thus provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity. | ||
:::+ FNS ET capacity is a good estimate of overal ET capacity in may cell types. | :::+ FNS ET capacity is a good estimate of overal ET capacity in may cell types. | ||
:::+ The presence of PMG and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity. | |||
:::+ Application of the cytochrome ''c'' test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of ''c''. | :::+ Application of the cytochrome ''c'' test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of ''c''. | ||
:::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | :::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | ||
:::- F OXPHOS capacity may be underestimated. In human heart muscle addition of Oct to palmitoylcarnitine (Pal) + malate increased OXPHOS by 26% (Lemuieux et al 2011). | |||
:::- SRot(E) may be underestimated if S is not saturating. | :::- SRot(E) may be underestimated if S is not saturating. | ||
:::- CIV activity is not measured, to save experimental time. | :::- CIV activity is not measured, to save experimental time. | ||
== Compare SUIT protocols == | == Compare SUIT protocols == | ||
::::* | ::::* | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 14 January 2019
Description
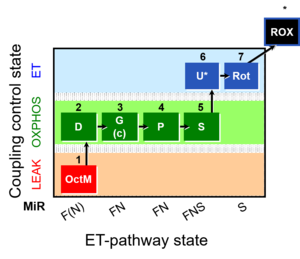
Abbreviation: FNS(Oct,PGM)
Reference: A Schoepf 2016 FEBS J
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT protocol,
SUIT B
- SUIT-category: FNS(Oct,PGM)
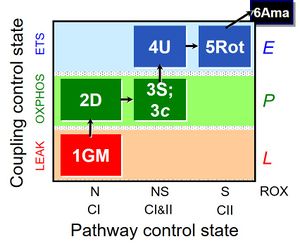
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral 1OctM;2D;3G;4P;5S;6U;7Rot
References
| Year | Reference | Organism | Tissue;cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schoepf 2016 FEBS J | 2016 | Schöpf B, Schäfer G, Weber A, Talasz H, Eder IE, Klocker H, Gnaiger E (2016) Oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial function differ between human prostate tissue and cultured cells. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13733 | Human | Endothelial;epithelial;mesothelial cell Genital Other cell lines Fibroblast |
Strengths and limitations
- + The protocol provides information on FAO capacity in the absence of other, potentially interfering pathways, both in the LEAK state and in OXPHOS.
- + FNS OXPHOS capacity comprises the most important pathways in many cell types and thus provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity.
- + FNS ET capacity is a good estimate of overal ET capacity in may cell types.
- + The presence of PMG and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity.
- + Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c.
- + Reasonable duration of the experiment.
- - F OXPHOS capacity may be underestimated. In human heart muscle addition of Oct to palmitoylcarnitine (Pal) + malate increased OXPHOS by 26% (Lemuieux et al 2011).
- - SRot(E) may be underestimated if S is not saturating.
- - CIV activity is not measured, to save experimental time.
Compare SUIT protocols
MitoPedia concepts: SUIT protocol, SUIT A