- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Glycerophosphate pathway control state
Description
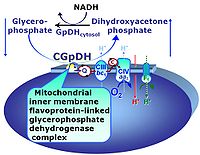
Gp: The glycero-phosphate shuttle represents an important pathway, particularly in liver, of making cytoplasmic NADH available for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Cytoplasmic NADH reacts with dihydroxyacetone phosphate catalyzed by cytoplasmic glycerophos-phate dehydrogenase. On the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane, mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase oxidises glycerophosphate back to dihydroxyacetone phosphate, a reaction not generating NADH but reducing a flavin prosthesic group. The reduced flavoprotein donates its reducing equivalents to the electron transfer system at the level of CoQ.
Abbreviation: Gp
Reference: Pathway control state, Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 4.4
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
SUIT state
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite
Gp(L)
Gp(P)
Gp(E)
Details
- Glycerophosphate oxidation is 10-fold higher in rabbit gracilis mitochondria (fast-twitch white muscle; 99% type IIb) compared to soleus (slow-twitch red muscle; 98% type I). Activity is comparatively low in human vastus lateralis. Glycerophosphate is an important substrate for respiration in brown adipose tissue mitochondria.