| Step
|
State
|
Pathway
|
Q-junction
|
Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
| 1OctM
|
OctML(n)
|
F(N)
|
FAO
|
1OctM
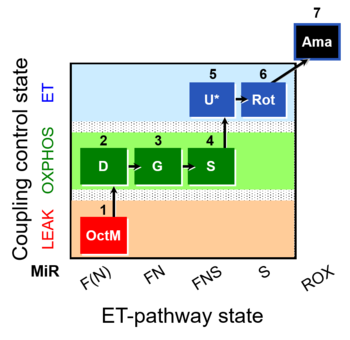
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. Low concentration of malate, typically 0.1 mM, does not saturate the N-pathway; but saturates the F-pathway. Non-phosphorylating resting state (LEAK state); LEAK respiration L(n) in the absence of ADP, ATP, AMP (no adenylates).
|
| 2D
|
OctMP
|
F(N)
|
FAO
|
1OctM;2D
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. Low concentration of malate, typically 0.1 mM, does not saturate the N-pathway; but saturates the F-pathway. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 3G
|
OctGMP
|
FN
|
F&CI
|
1OctM;2D;3G
|
| 4S
|
OctGMSP
|
FNS
|
F&CI&II
|
1OctM;2D;3G;4S
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of type N substrates & succinate, with convergent electron flow in the NS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function. Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 5U
|
OctGMSE
|
FNS
|
F&CI&II
|
1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5U
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of type N substrates & succinate, with convergent electron flow in the NS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function. Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E.
|
| 6Rot
|
SE
|
S
|
CII
|
1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot
|
| 7Ama
|
ROX
|
|
|
1OctM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama
- Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated either after inhibition of CIII (e.g. antimycin A, myxothiazol), CIV (e.g. Cyanide) or in the absence of endogenous fuel-substrates. Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration.
|