Difference between revisions of "N-junction"
From Bioblast
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|description=[[File:SUIT-catg N.jpg|right|300px|N-junction]] | |description=[[File:SUIT-catg N.jpg|right|300px|N-junction]] | ||
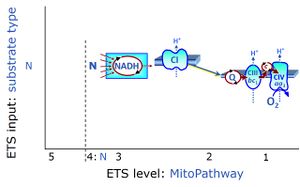
The '''N-junction''' is a junction for [[convergent electron flow]] in the [[electron transfer system]] (ETS) from type N substrates (''further details'' »[[N-pathway control]]) through the mt-[[NADH]] pool to [[Complex I]] (CI), and further transfer through the [[Q-junction]] to [[Complex III]] (CIII). Representative type N substrates are pyruvate, glutamate and malate. The corresponding dehydrogenases (PDH, GDH, MDH) generate NADH, the substrate of [[Complex I]] (CI). The concept of the N-junction and [[F-junction]] provides a basis for defining [[categories of SUIT protocols]] based on [[pathway control state]]s. | The '''N-junction''' is a junction for [[convergent electron flow]] in the [[electron transfer system]] (ETS) from type N substrates (''further details'' »[[N-pathway control state]]) through the mt-[[NADH]] pool to [[Complex I]] (CI), and further transfer through the [[Q-junction]] to [[Complex III]] (CIII). Representative type N substrates are pyruvate, glutamate and malate. The corresponding dehydrogenases (PDH, GDH, MDH) generate NADH, the substrate of [[Complex I]] (CI). The concept of the N-junction and [[F-junction]] provides a basis for defining [[categories of SUIT protocols]] based on [[pathway control state]]s. | ||
|info=[[N-pathway control]] | |info=[[N-pathway control state]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
Revision as of 19:07, 7 November 2016
Description
The N-junction is a junction for convergent electron flow in the electron transfer system (ETS) from type N substrates (further details »N-pathway control state) through the mt-NADH pool to Complex I (CI), and further transfer through the Q-junction to Complex III (CIII). Representative type N substrates are pyruvate, glutamate and malate. The corresponding dehydrogenases (PDH, GDH, MDH) generate NADH, the substrate of Complex I (CI). The concept of the N-junction and F-junction provides a basis for defining categories of SUIT protocols based on pathway control states.
Reference: N-pathway control state
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT concept
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
Contributed by Gnaiger E 2016-02-12; edited 2016-08-28.