Description
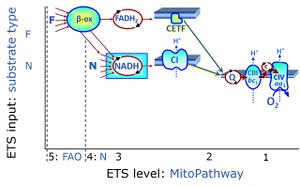
FN is induced in mt-preparations by addition of NADH-generating substrates (N-pathway control state, or CI-linked pathway control) in combination with one or several fatty acids, which are supplied to feed electrons into the F-junction through fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (reduced form FADH2), to electron transferring flavoprotein (CETF), and further through the Q-junction to Complex III (CIII). FAO not only depends on electron transfer through the F-junction (which is typically rate-limiting), but simultaneously generates FADH2 and NADH and thus depends on N-junction throughput. Hence FAO can be inhibited completely by inhibition of Complex I (CI). This physiological substrate combination is required for partial reconstitution of TCA cycle function and convergent electron-input into the Q-junction, to compensate for metabolite depletion into the incubation medium. FS in combination exerts an additive effect of convergent electron flow in most types of mitochondria.
Abbreviation: FN
Reference: Electron-transfer-pathway state, Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger E, edited 2019-01-22 by Komlodi T.
FNL
FN pathway in the LEAK state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
FNP
FN pathway in the OXPHOS state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
-
- DL-Protocol for isolated mitochondria and tissue homogenate (mt): SUIT-002 O2 mt D005
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized fibers (pfi): SUIT-002 O2 pfi D006
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-002 O2 ce-pce D007
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized fibers (pfi):SUIT-005 O2 pfi D011
-
FNE
FN pathway in the ET state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
SUIT state,
Recommended
MitoPedia topics:
EAGLE