Template:SUIT-024 O2 ce-pce D056
From Bioblast
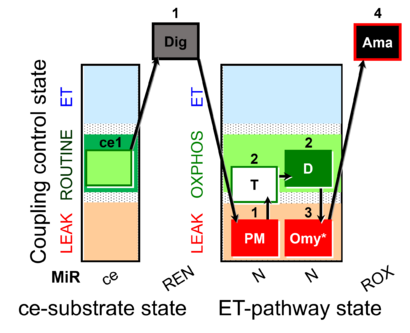
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ce1 | ROUTINE | ce1
| ||
| 1Dig | REN | ce1;1Dig
|
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2T | PML or PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D
|
| 3Omy | PML(Omy) | 1PM;2T;2D;3Omy
| ||
| 4Ama | ROX | 1PM;2T;2D;3Omy;4Ama
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary