Description
Abbreviation: FAO and NSGp-pathways
Reference: A - SUIT-040 - F-pathway and NSGp-pathway
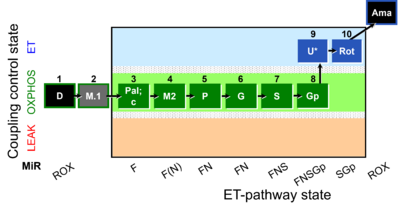
SUIT number: D094_1D;2M.1;3Pal;3c;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama
The SUIT-040 O2 mt D094 protocol provides a common reference for comparison of respiratory control of mitochondrial preparations such as isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenates and permeabilized cells (already permeabilized when they are added to the chamber) in a wide variety of species, tissues and cell types. SUIT-040 O2 mt D094 is specially designed to give information on F-pathway with palmitoylcarnitine as a FAO substrate in OXPHOS state avoiding FAO overestimation in the presence of anaplerotic pathways. Moreover, the pathway control in OXPHOS state (F, F(N), FN, FNS, FNSGp pathways) and in ET state (FNSGp and SGp) can be evaluated by using this SUIT protocol.
Communicated by Grings M, Cecatto C and Cardoso LHD (last update 2023-04-12)
Representative traces
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D | ROX | 1D
| ||
| 2M.1 | 1D;2M.1 | |||
| 3Pal | PalMP | F | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Pal
|
| 3c | PalMcP | F | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;3c
|
| 4M2 | PalMP | F(N) | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;3c;4M2
|
| 5P | PalPMP | FN | FAO&CI | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P
|
| 6G | PalPGMP | FN | FAO&CI | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G
|
| 7S | PalPGMSP | FNS | FAO&CI&II | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G;7S
|
| 8Gp | PalPGMSGpP | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp
|
| 9U | PalPGMSGpE | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U
|
| 10Rot | SGpE | SGp | CII&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot
|
| 11Ama | ROX | 1D;2M.1;3Pal;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- SUIT-040 allows assessing FAO-linked respiration avoiding overestimation by endogenous substrates or malate anaplerosis. Other electron transfer pathways are also analyzed in OXPHOS (FN, FNS, FNSGp) and ET-state (FNSGp, SGp).
- + SUIT-039 allows the depletion of endogenous substrates with ADP (1D).
- + The protocol provides information on F-pathway in OXPHOS state with palmitoylcarnitine, a long-chain acylcarnitine commonly found in vivo.
- + The low concentration of malate used in this protocol to assess F-pathway, typically 0.1 mM, does not saturate the N-pathway; but saturates the F-pathway.
- + F-pathway (3Pal-2M.1) can be compared to FN-pathway (5P) in OXPHOS state.
- + Pathway control in OXPHOS (F, F(N), FN, FNS, FNSGp pathways) and in ET state (FNSGp and SGp) can be observed.
- + Multiple pathways converging into Q (FNSGp) are assessed in OXPHOS and ET states. Therefore, P/E (8Gp/9U) at high ET capacity can be calculated.
- - Long duration of the experiment.
- - LEAK state is not investigated.
Compare SUIT protocols
- SUIT-036_O2_mt_D089: Similar protocol, including malate kinetics to assess mitochondrial malic enzyme and anaplerosis.
- SUIT-002 O2 mt D005: Reference protocol SUIT protocol for isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenate and permeabilized cells (already permeabilized). Allows evaluation of FAO with octanoylcarnitine, also without overestimation by using low malate concentration. Besides this, provides information on pathway control in OXPHOS state (F, F(N), FN, FNS, FNSGp pathways) and ET-state (FNSGp, SGp pathways).
- SUIT-025_O2_mt_D057: Allows evaluation of FAO with octanoylcarnitine, also without overestimation by using low malate concentration. Besides this, provides information on pathway control in OXPHOS state (F, F(N), FN, FNS pathways).
- SUIT-041 O2 mt D096: A protocol to determine the optimum concentration of acylcarnitine.
Chemicals and syringes
| Step | Chemical(s) and link(s) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1D | ADP (D) | |
| 2M.1 | Malate (M) | |
| 3Pal | Palmitoylcarnitine (Pal) | |
| 3c | Cytochrome c (c) | |
| 4M2 | Malate (M) | |
| 5P | Pyruvate (P) | |
| 6G | Glutamate (G) | |
| 7S | Succinate (S) | |
| 8Gp | Glycerophosphate (Gp) | |
| 9U | Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone, CCCP (U) | Can be substituted for other uncoupler |
| 10Rot | Rotenone (Rot) | |
| 11Ama | Antimycin A (Ama) |
- Suggested stock concentrations are shown in the specific DL-Protocol.
References
- The project FAT4BRAIN has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 857394
Labels:
FAT4BRAINSUIT