Boukalova 2020 Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis
| Boukalova S, Hubackova S, Milosevic M, Ezrova Z, Neuzil J, Rohlena J (2020) Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in oxidative phosphorylation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866:165759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165759 |
Boukalova Stepana, Hubackova S, Milosevic M, Ezrova Z, Neuzil J, Rohlena J (2020) Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis
Abstract: Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is an enzyme of the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway that provides nucleotides for RNA/DNA synthesis essential for proliferation. In mammalian cells, DHODH is localized in mitochondria, linked to the respiratory chain via the coenzyme Q pool. Here we discuss the role of DHODH in the oxidative phosphorylation system and in the initiation and progression of cancer. We summarize recent findings on DHODH biology, the progress made in the development of new, specific inhibitors of DHODH intended for cancer therapy, and the mechanistic insights into the consequences of DHODH inhibition.
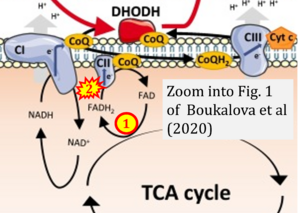
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«