Anoar 2021 Front Neurosci
| Anoar S, Woodling NS, Niccoli T (2021) Mitochondria dysfunction in frontotemporal dementia/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: lessons from Drosophila models. Front Neurosci 15:786076. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.786076 |
Anoar S, Woodling NS, Niccoli T (2021) Front Neurosci
Abstract: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by declining motor and cognitive functions. Even though these diseases present with distinct sets of symptoms, FTD and ALS are two extremes of the same disease spectrum, as they show considerable overlap in genetic, clinical and neuropathological features. Among these overlapping features, mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with both FTD and ALS. Recent studies have shown that cells derived from patients' induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)s display mitochondrial abnormalities, and similar abnormalities have been observed in a number of animal disease models. Drosophila models have been widely used to study FTD and ALS because of their rapid generation time and extensive set of genetic tools. A wide array of fly models have been developed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of toxicity for mutations associated with FTD/ALS. Fly models have been often instrumental in understanding the role of disease associated mutations in mitochondria biology. In this review, we discuss how mutations associated with FTD/ALS disrupt mitochondrial function, and we review how the use of Drosophila models has been pivotal to our current knowledge in this field.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
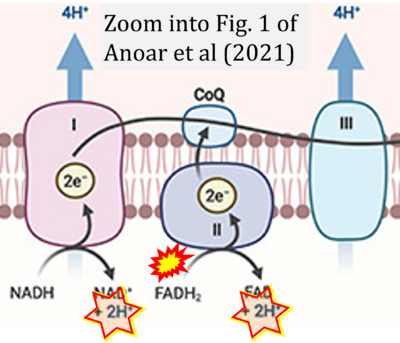
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Hydrogen ion ambiguities in the electron transfer system
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2023-10-08) last update 2023-11-10
- Electron (e-) transfer linked to hydrogen ion (hydron; H+) transfer is a fundamental concept in the field of bioenergetics, critical for understanding redox-coupled energy transformations.
- However, the current literature contains inconsistencies regarding H+ formation on the negative side of bioenergetic membranes, such as the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane, when NADH is oxidized during oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Ambiguities arise when examining the oxidation of NADH by respiratory Complex I or succinate by Complex II.
- Oxidation of NADH or succinate involves a two-electron transfer of 2{H++e-} to FMN or FAD, respectively. Figures indicating a single electron e- transferred from NADH or succinate lack accuracy.
- The oxidized NAD+ is distinguished from NAD indicating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide independent of oxidation state.
- NADH + H+ → NAD+ +2{H++e-} is the oxidation half-reaction in this H+-linked electron transfer represented as 2{H++e-} (Gnaiger 2023). Putative H+ formation shown as NADH → NAD+ + H+ conflicts with chemiosmotic coupling stoichiometries between H+ translocation across the coupling membrane and electron transfer to oxygen. Ensuring clarity in this complex field is imperative to tackle the apparent ambiguity crisis and prevent confusion, particularly in light of the increasing number of interdisciplinary publications on bioenergetics concerning diagnostic and clinical applications of OXPHOS analysis.
Labels: Pathology: Neurodegenerative
Organism: Drosophila
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase