Description
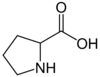
Proline (Pro), C5H9NO2, is an amino acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly in the nonpolar form, with pKa1 = 1.99 pKa2 = 10.96. Proline is an anaplerotic substrate that supports both the proline pathway control state and the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state. Proline is used as a single substrate or in combination with carbohydrate-derived metabolites in mitochondria particularly of flight muscle of many (but not all) insects. Proline is oxidized to delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate by the mtIM L-proline:quinone oxidoreductase (proline dehydrogenase, ProDH), with reduction of FAD to FADH2 and direct entry into the Q-junction. delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate is converted to glutamate by 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase.
Abbreviation: Pro
Reference: PubChem, Teulier 2016 Proc Biol Sci, Soares 2015 PLoS One
Communicated by Garcia-Souza LF and Gnaiger E 2019-04-29
Application in HRR
- Preparation of 2 M stock solution (dissolved in H2O; M.W. = 115.13)
- Weigh 1.1513 g L-proline and transfer to a 5 mL volumetric glass flask.
- Add to 5 mL of H2O and divide into 0.5 mL portions.
- Store at -20 °C.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume: 10 µL using a 25 µl syringe (2 mL O2k-Chamber).
- Final concentration: 10 mM.
References
- Teulier L, Weber JM, Crevier J, Darveau CA (2016) Proline as a fuel for insect flight: enhancing carbohydrate oxidation in hymenopterans. Proc Biol Sci 283: 20160333. - »Bioblast link«
MitoPedia topics: Substrate and metabolite