From Bioblast
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Description
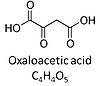
Oxaloacetic acid, C4H4O5, occurs under physiological conditions as the anion oxaloacetate2-, Oa. Oxaloacetate is formed from malate by MDH. Oa reacts with acetyl-CoA through citrate synthase to form citrate, or with glutamate through transaminase to form oxoglutarate and aspartate. Oa transport is restricted across the inner mt-membrane of various tissues. Oa is a potent inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase.
Abbreviation: Oa
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite