Categories of SUIT protocols: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|abbr=SUITp-Catg | |abbr=SUITp-Catg | ||
|description='''Categories of SUIT protocols''' group '''SUIT protocols''' according to all [[substrate types]] involved in a protocol, independent of titrations of inhibitors which block the oxidation of the substrates present. ROX states may or may not be included in a SUIT protocol, which does not change its category. | |description='''Categories of SUIT protocols''' group '''SUIT protocols''' according to all [[substrate types]] involved in a protocol, independent of titrations of inhibitors which block the oxidation of the substrates present. ROX states may or may not be included in a SUIT protocol, which does not change its category. | ||
|info=[[MiPNet21.06 SUIT reference assay]] | |||
}} | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | |||
|mitopedia concept=MitoFit Quality Control System | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | {{MitoPedia methods}} | ||
{{MitoPedia SUIT | {{MitoPedia SUIT | ||
Revision as of 07:36, 1 February 2016
Description
Categories of SUIT protocols group SUIT protocols according to all substrate types involved in a protocol, independent of titrations of inhibitors which block the oxidation of the substrates present. ROX states may or may not be included in a SUIT protocol, which does not change its category.
Abbreviation: SUITp-Catg
Reference: MiPNet21.06 SUIT reference assay
MitoPedia concepts: "MitoFit Quality Control System" is not in the list (MiP concept, Respiratory state, Respiratory control ratio, SUIT concept, SUIT protocol, SUIT A, SUIT B, SUIT C, SUIT state, Recommended, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia concept" property.
MitoFit Quality Control System"MitoFit Quality Control System" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
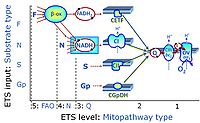
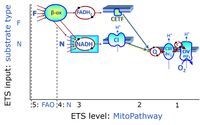
Categorization of SUIT protocols: substrate types
There are many ways to define groups of SUIT protocols. Since the complexity of SUIT protocols is primarily determined by the large number of possible substrate states, and to a lesser extent by the smaller number of possible coupling states, a relevant type of categories of SUIT protocols considers the substrate types involved.
At the present stage of development of the 'library of SUIT protocols' as part of the MitoFit Quality Control System, five substrate types are considered:
- On the pathway level of converging NADH- and FADH2-linked dehydrogenases, including the TCA cycle and beta-oxidation:
- On the pathway level of electron transfer complexes converging at the Q-junction:
- S: Succinate (CII-linked)
- Gp: Glycerophosphate (CGpDH-linked)
- On the single step level of cytochrome c oxidase (CIV), the terminal step in the aerobic electron transfer system:
- Tm: Artificial electron transfer susbstrate TMPD (Tm) maintained in a reduced state by ascorbate (As) and reducing cytochrome c as the substrate of CIV.
SUITp-Catg: single substrate type
- N - ETS-level 4
- F - ETS-level 4
- S - ETS-level 3
- Gp - ETS-level 3
- Tm - ETS-level 1. Tm can always be included or excluded at the end of a SUIT protocol. To simplify the categorization, Tm is not considered in this system of SUIT protocols.
SUITp-Catg: multiple substrate types with NS
NS
NFS
NSGp
NFSGp
SUITp-Catg: multiple substrate types with N (without S)
NF
NGp
NFGp
SUITp-Catg: multiple substrate types without N
- F and S without N are problematic substrate states due to accumulation of Oxa or Acetyl-CoA. Therefore, addition of malate alone (M without P or G) is not considered as substrate type N. However, high mt-malic enzyme activity requires a change of this concept, when M alone represents an ETS ccompetent substrate state. Low concentration of M may be used to support FAO, whereas a higher concentration of M may be required for N-linked respiratory capacity to override FAO capacity; this needs corresponding kinetic analyses (SUIT test protocols).